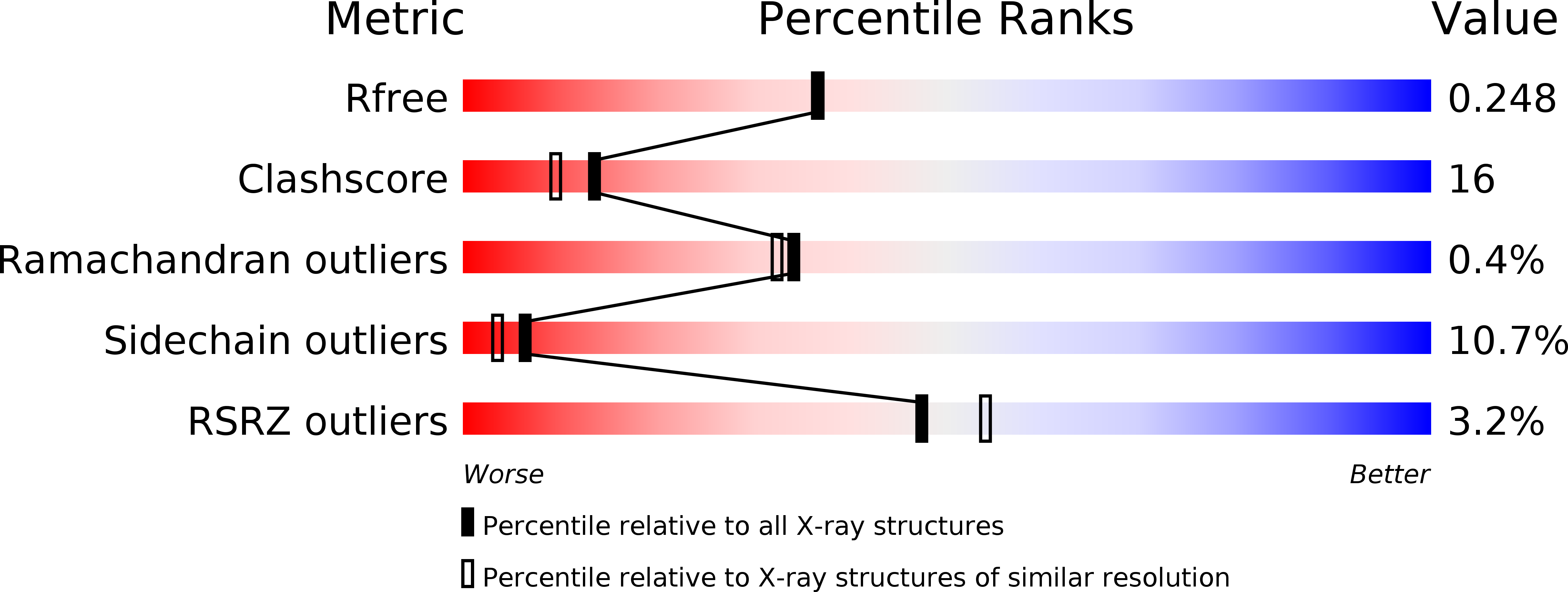
Stable MOB1 interaction with Hippo/MST is not essential for development and tissue growth control.
Kulaberoglu, Y., Lin, K., Holder, M., Gai, Z., Gomez, M., Assefa Shifa, B., Mavis, M., Hoa, L., Sharif, A.A.D., Lujan, C., Smith, E.S.J., Bjedov, I., Tapon, N., Wu, G., Hergovich, A.(2017) Nat Commun 8: 695-695
- PubMed: 28947795
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00795-y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5XQZ - PubMed Abstract:
The Hippo tumor suppressor pathway is essential for development and tissue growth control, encompassing a core cassette consisting of the Hippo (MST1/2), Warts (LATS1/2), and Tricornered (NDR1/2) kinases together with MOB1 as an important signaling adaptor. However, it remains unclear which regulatory interactions between MOB1 and the different Hippo core kinases coordinate development, tissue growth, and tumor suppression. Here, we report the crystal structure of the MOB1/NDR2 complex and define key MOB1 residues mediating MOB1's differential binding to Hippo core kinases, thereby establishing MOB1 variants with selective loss-of-interaction. By studying these variants in human cancer cells and Drosophila, we uncovered that MOB1/Warts binding is essential for tumor suppression, tissue growth control, and development, while stable MOB1/Hippo binding is dispensable and MOB1/Trc binding alone is insufficient. Collectively, we decrypt molecularly, cell biologically, and genetically the importance of the diverse interactions of Hippo core kinases with the pivotal MOB1 signal transducer.The Hippo tumor suppressor pathway is essential for development and tissue growth control. Here the authors employ a multi-disciplinary approach to characterize the interactions of the three Hippo kinases with the signaling adaptor MOB1 and show how they differently affect development, tissue growth and tumor suppression.
Organizational Affiliation:
Tumour Suppressor Signalling Network Laboratory, UCL Cancer Institute, University College London, London, WC1E 6BT, UK.