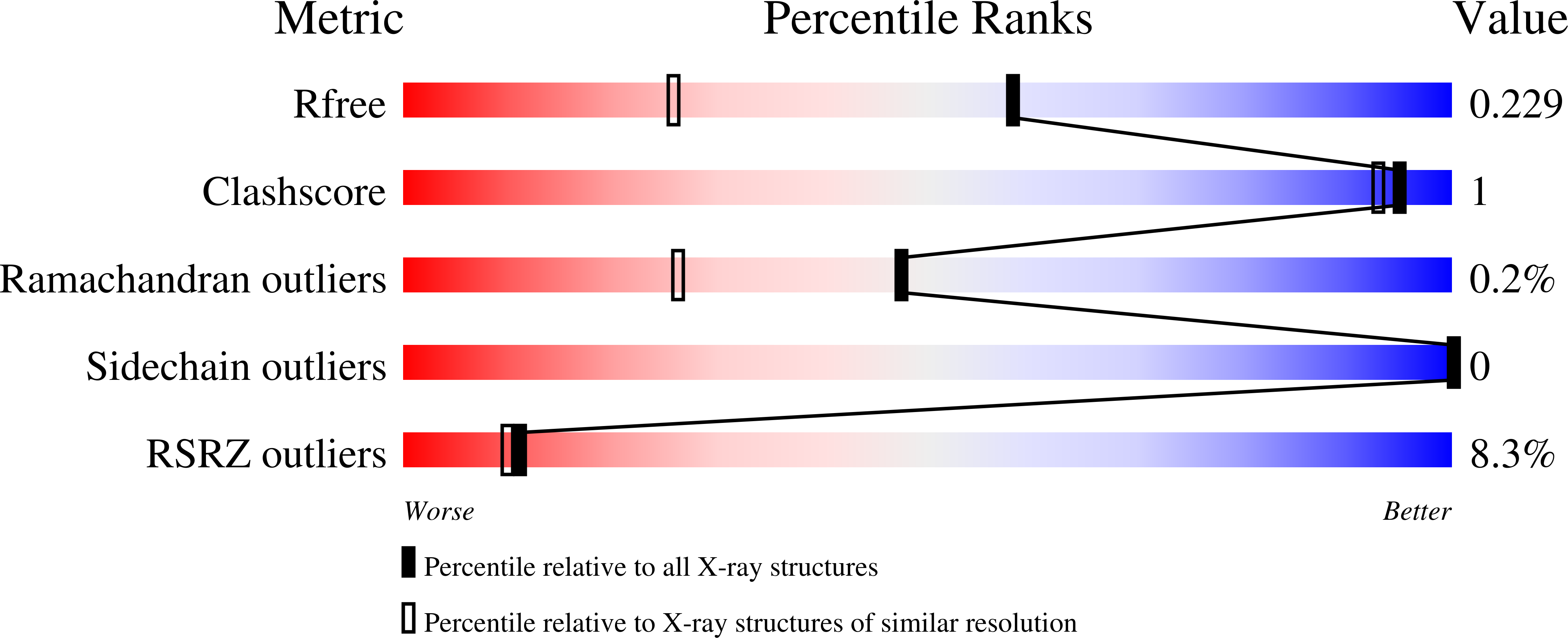
Identification of a PDE4-Specific Pocket for the Design of Selective Inhibitors.
Feng, X., Wang, H., Ye, M., Xu, X.T., Xu, Y., Yang, W., Zhang, H.T., Song, G., Ke, H.(2018) Biochemistry 57: 4518-4525
- PubMed: 29975048
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00336
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5WH5, 5WH6 - PubMed Abstract:
Inhibitors of phosphodiesterases (PDEs) have been widely studied as therapeutics for the treatment of human diseases, but improvement of inhibitor selectivity is still desirable for the enhancement of inhibitor potency. Here, we report identification of a water-containing subpocket as a PDE4-specific pocket for inhibitor binding. We designed against the pocket and synthesized two enantiomers of PDE4 inhibitor Zl-n-91. The ( S)-Zl-n-91 enantiomer showed IC 50 values of 12 and 20 nM for the catalytic domains of PDE4D2 and PDE4B2B, respectively, selectivity several thousand-fold greater than those of other PDE families, and potent neuroprotection activities. Crystal structures of the PDE4D2 catalytic domain in complex with each Zl-n-91 enantiomer revealed that ( S)-Zl-n-91 but not ( R)-Zl-n-91 formed a hydrogen bond with the bound water in the pocket, thus explaining its higher affinity. The structural superposition between the PDE families revealed that this water-containing subpocket is unique to PDE4 and thus valuable for the design of PDE4 selective inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Pharmaceutical Engineering and Life Sciences , Changzhou University , Changzhou , Jiangsu 213164 , P. R. China.