Molecular basis of human CD22 function and therapeutic targeting.
Ereno-Orbea, J., Sicard, T., Cui, H., Mazhab-Jafari, M.T., Benlekbir, S., Guarne, A., Rubinstein, J.L., Julien, J.P.(2017) Nat Commun 8: 764-764
- PubMed: 28970495
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00836-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5VKJ, 5VKK, 5VKM, 5VL3 - PubMed Abstract:
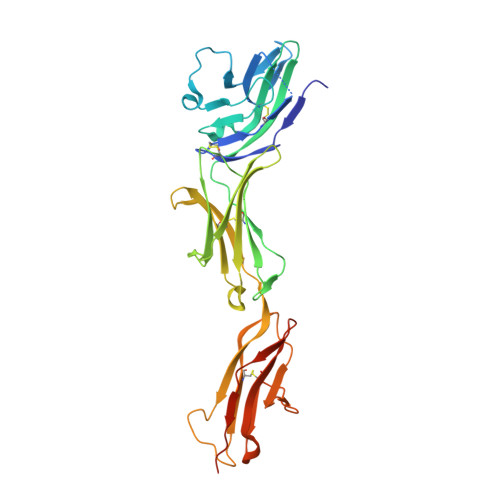
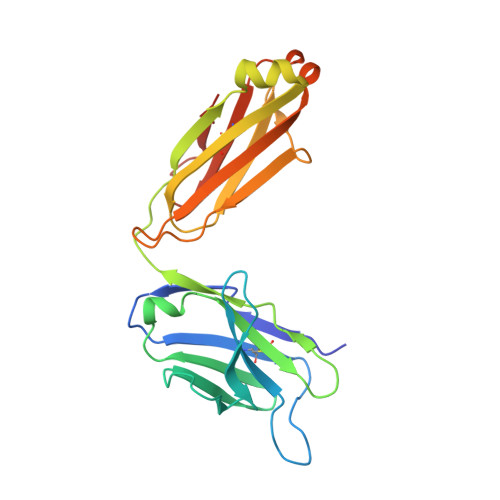
CD22 maintains a baseline level of B-cell inhibition to keep humoral immunity in check. As a B-cell-restricted antigen, CD22 is targeted in therapies against dysregulated B cells that cause autoimmune diseases and blood cancers. Here we report the crystal structure of human CD22 at 2.1 Å resolution, which reveals that specificity for α2-6 sialic acid ligands is dictated by a pre-formed β-hairpin as a unique mode of recognition across sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectins. The CD22 ectodomain adopts an extended conformation that facilitates concomitant CD22 nanocluster formation on B cells and binding to trans ligands to avert autoimmunity in mammals. We structurally delineate the CD22 site targeted by the therapeutic antibody epratuzumab at 3.1 Å resolution and determine a critical role for CD22 N-linked glycosylation in antibody engagement. Our studies provide molecular insights into mechanisms governing B-cell inhibition and valuable clues for the design of immune modulators in B-cell dysfunction.The B-cell-specific co-receptor CD22 is a therapeutic target for depleting dysregulated B cells. Here the authors structurally characterize the ectodomain of CD22 and present its crystal structure with the bound therapeutic antibody epratuzumab, which gives insights into the mechanism of inhibition of B-cell activation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Program in Molecular Medicine, The Hospital for Sick Children Research Institute, Toronto, ON, Canada, M5G 0A4.