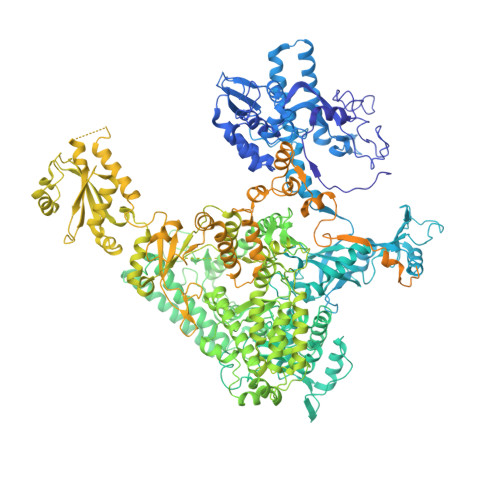
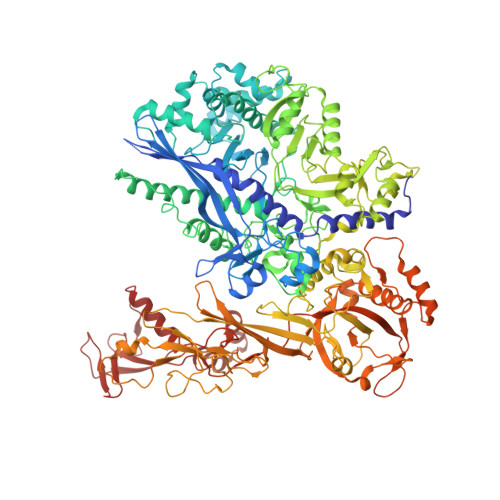
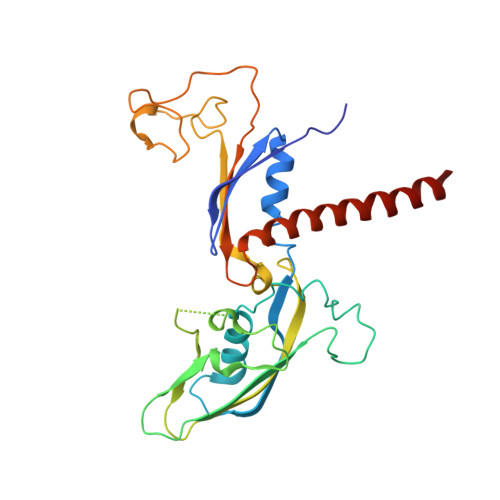
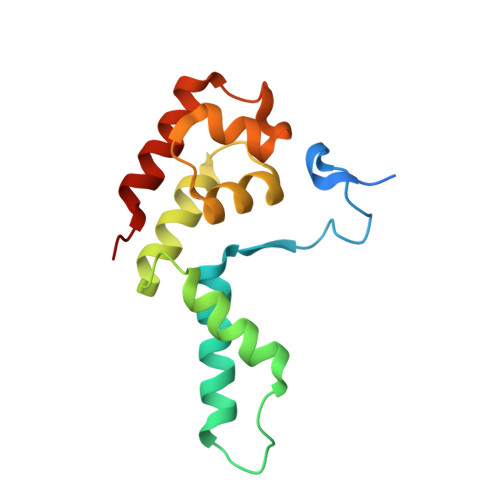
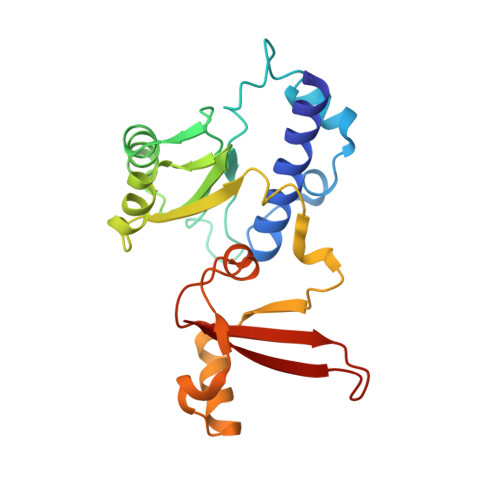
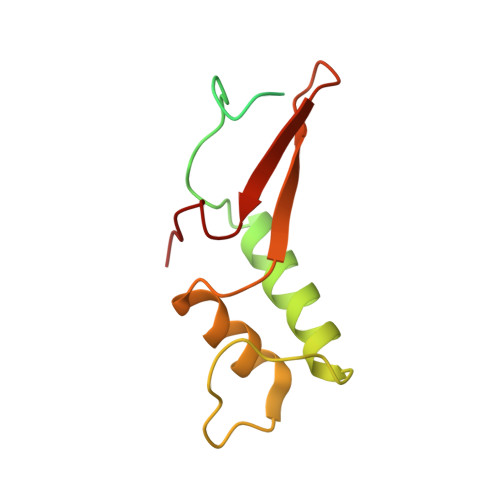
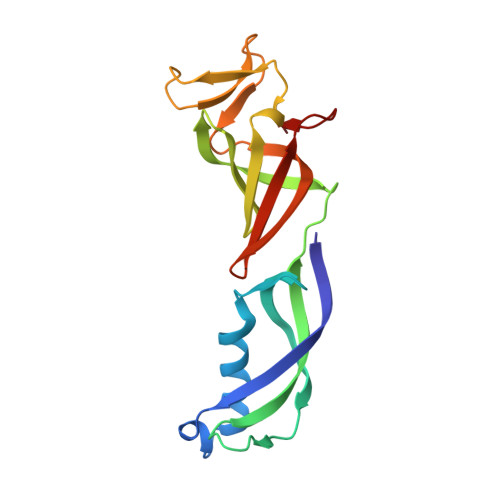
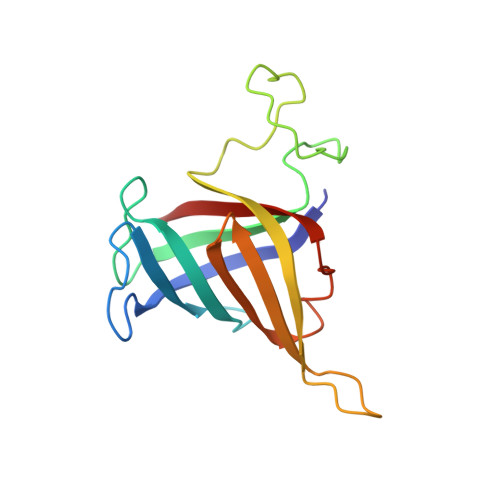
Structure of a transcribing RNA polymerase II-DSIF complex reveals a multidentate DNA-RNA clamp.
Bernecky, C., Plitzko, J.M., Cramer, P.(2017) Nat Struct Mol Biol 24: 809-815
- PubMed: 28892040
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3465
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5OHO, 5OHQ, 5OIK - PubMed Abstract:
During transcription, RNA polymerase II (Pol II) associates with the conserved elongation factor DSIF. DSIF renders the elongation complex stable and functions during Pol II pausing and RNA processing. We combined cryo-EM and X-ray crystallography to determine the structure of the mammalian Pol II-DSIF elongation complex at a nominal resolution of 3.4 Å. Human DSIF has a modular structure with two domains forming a DNA clamp, two domains forming an RNA clamp, and one domain buttressing the RNA clamp. The clamps maintain the transcription bubble, position upstream DNA, and retain the RNA transcript in the exit tunnel. The mobile C-terminal region of DSIF is located near exiting RNA, where it can recruit factors for RNA processing. The structure provides insight into the roles of DSIF during mRNA synthesis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen, Germany.