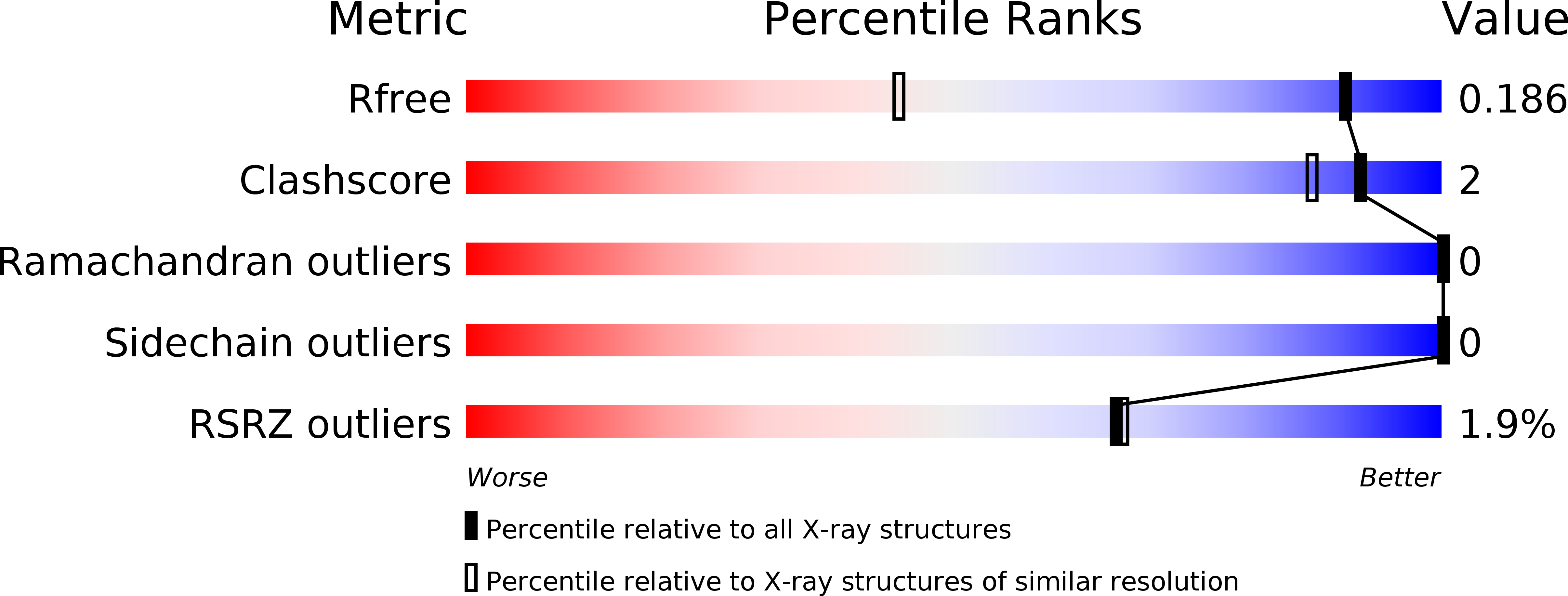
1,3-Oxazole-based selective picomolar inhibitors of cytosolic human carbonic anhydrase II alleviate ocular hypertension in rabbits: Potency is supported by X-ray crystallography of two leads.
Ferraroni, M., Lucarini, L., Masini, E., Korsakov, M., Scozzafava, A., Supuran, C.T., Krasavin, M.(2017) Bioorg Med Chem 25: 4560-4565
- PubMed: 28728897
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2017.06.054
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5NEA, 5NEE - PubMed Abstract:
Two lead 1,3-oxazole-based carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs) earlier identified as selective, picomolar inhibitors of hCA II (a cytosolic target for treatment of glaucoma) have been investigated further. Firstly, they were found to be conveniently synthesized on multigram scale, which enables further development. These compounds were found to be comparable in efficacy to dorzolamide eye drops when applied in the eye drop form as well. Finally, the reasons for unusually high potency of these compounds became understood from their high-resolution X-ray crystallography structures. These data significantly expand our understanding of heterocycle-based primary sulfonamides, many of which have recently emerged from our labs - particularly, from the corneal permeability standpoint.
Organizational Affiliation:
Chemistry Dept., Universita degli Studi di Firenze, Florence 50019, Italy.