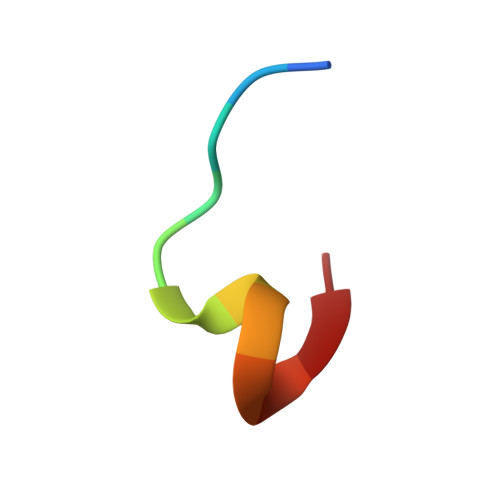
Structural basis for multi-specific peptide recognition by the anti-IDH1/2 monoclonal antibody, MsMab-1.
Kitago, Y., Kaneko, M.K., Ogasawara, S., Kato, Y., Takagi, J.(2016) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 478: 1274-1279
- PubMed: 27553275
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.110
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5GIR, 5GIS - PubMed Abstract:
A point mutation in isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) and IDH2 is directly linked to the pathogenesis of certain types of tumors. To detect this mutation, several antibodies that can distinguish between mutant and wild-type enzymes have been established. One of which, MsMab-1, has a unique multi-specific character against several types of mutated IDH1/2. This promiscuous character is in remarkable contrast to the highly specific antigen recognition typically observed with a monoclonal antibody. We solved the crystal structure of MsMab-1 Fab fragment in complex with either IDH1 or IDH2-derived peptides. Based on the structure, it became clear that the peptide-binding pocket of the antibody is highly complementary to the core determinant shared between the IDH1 and IDH2, while leaving just enough space for the side chain of the pathogenic but not the wild-type amino acids located in the mutation position. Clarification of the molecular basis for the peculiar binding characteristics of MsMab-1 in atomic detail will help facilitating its diagnostic application, and may be used to develop better diagnostic reagents through structure-guided protein engineering.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Protein Synthesis and Expression, Institute for Protein Research, Osaka University, 3-2 Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka 565-0871, Japan.