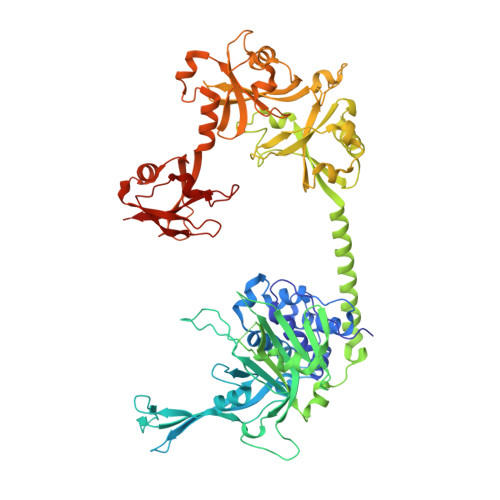
Structure of Usp7 Catalytic Domain and Three Ubl-Domains Reveals a Connector Alpha-Helix with Regulatory Role.
Kim, R.Q., Van Dijk, W.J., Sixma, T.K.(2016) J Struct Biol 195: 11
- PubMed: 27183903
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2016.05.005
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
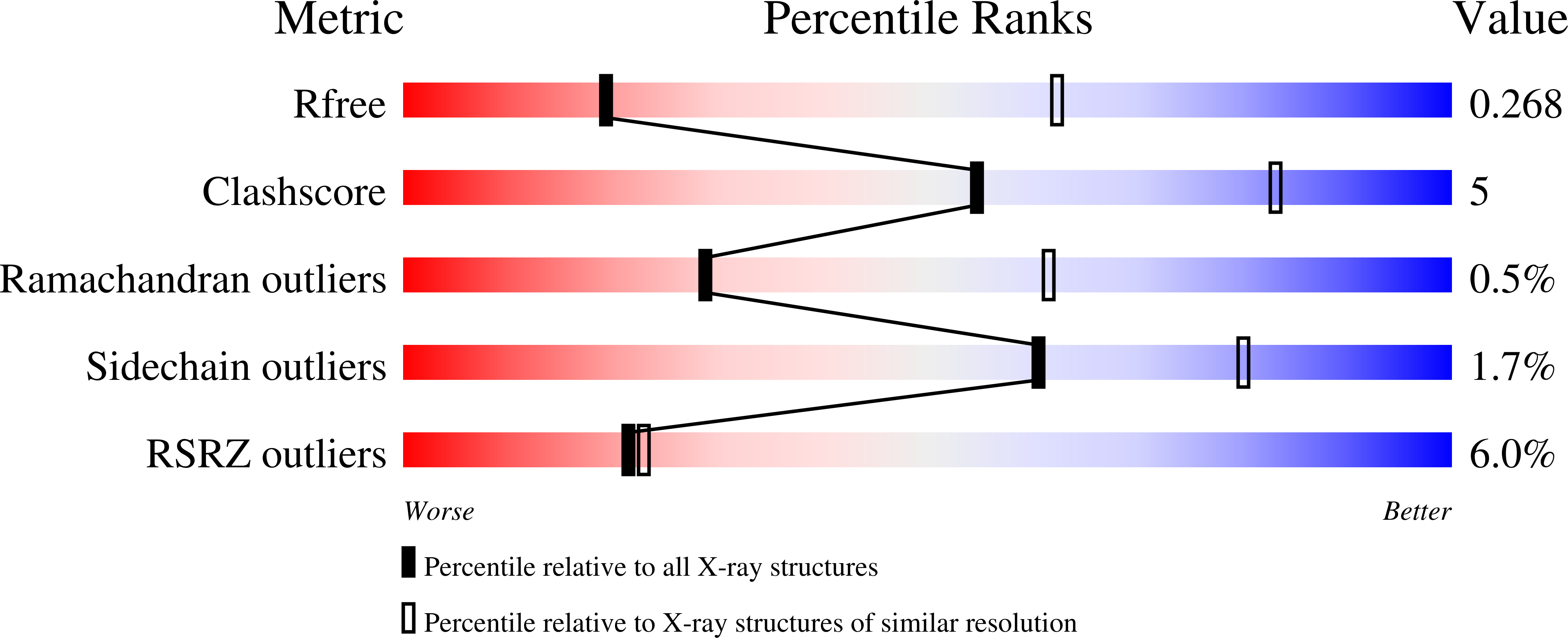
5FWI - PubMed Abstract:
Ubiquitin conjugation is an important signal in cellular pathways, changing the fate of a target protein, by degradation, relocalisation or complex formation. These signals are balanced by deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs), which antagonize ubiquitination of specific protein substrates. Because ubiquitination pathways are critically important, DUB activity is often carefully controlled. USP7 is a highly abundant DUB with numerous targets that plays complex roles in diverse pathways, including DNA regulation, p53 stress response and endosomal protein recycling. Full-length USP7 switches between an inactive and an active state, tuned by the positioning of 5 Ubl folds in the C-terminal HUBL domain. The active state requires interaction between the last two Ubls (USP7(45)) and the catalytic domain (USP7(CD)), and this can be promoted by allosteric interaction from the first 3 Ubl domains of USP7 (USP7(123)) interacting with GMPS. Here we study the transition between USP7 states. We provide a crystal structure of USP7(CD123) and show that CD and Ubl123 are connected via an extended charged alpha helix. Mutational analysis is used to determine whether the charge and rigidity of this 'connector helix' are important for full USP7 activity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Biochemistry and Cancer Genomics Center, Netherlands Cancer Institute, Plesmanlaan 121, 1066 CX Amsterdam, The Netherlands.