Structural Basis for Simvastatin Competitive Antagonism of Complement Receptor 3.
Jensen, M.R., Bajic, G., Zhang, X., Laustsen, A.K., Kolds, H., Skeby, K.K., Schitt, B., Andersen, G.R., Vorup-Jensen, T.(2016) J Biol Chem 291: 16963-16976
- PubMed: 27339893
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.732222
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
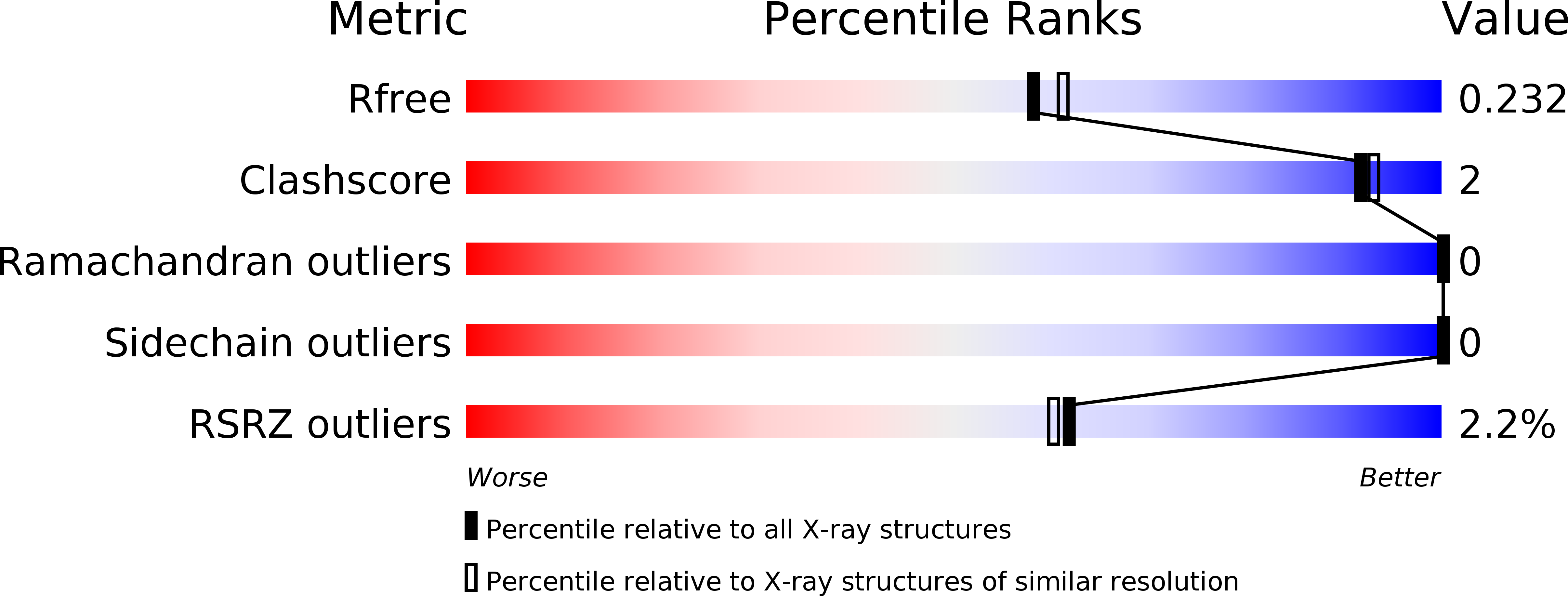
4XW2 - PubMed Abstract:
The complement system is an important part of the innate immune response to infection but may also cause severe complications during inflammation. Small molecule antagonists to complement receptor 3 (CR3) have been widely sought, but a structural basis for their mode of action is not available. We report here on the structure of the human CR3 ligand-binding I domain in complex with simvastatin. Simvastatin targets the metal ion-dependent adhesion site of the open, ligand-binding conformation of the CR3 I domain by direct contact with the chelated Mg(2+) ion. Simvastatin antagonizes I domain binding to the complement fragments iC3b and C3d but not to intercellular adhesion molecule-1. By virtue of the I domain's wide distribution in binding kinetics to ligands, it was possible to identify ligand binding kinetics as discriminator for simvastatin antagonism. In static cellular experiments, 15-25 μm simvastatin reduced adhesion by K562 cells expressing recombinant CR3 and by primary human monocytes, with an endogenous expression of this receptor. Application of force to adhering monocytes potentiated the effects of simvastatin where only a 50-100 nm concentration of the drug reduced the adhesion by 20-40% compared with untreated cells. The ability of simvastatin to target CR3 in its ligand binding-activated conformation is a novel mechanism to explain the known anti-inflammatory effects of this compound, in particular because this CR3 conformation is found in pro-inflammatory environments. Our report points to new designs of CR3 antagonists and opens new perspectives and identifies druggable receptors from characterization of the ligand binding kinetics in the presence of antagonists.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Departments of Biomedicine.