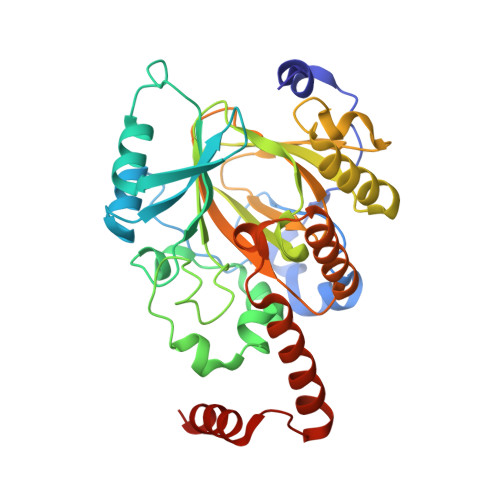
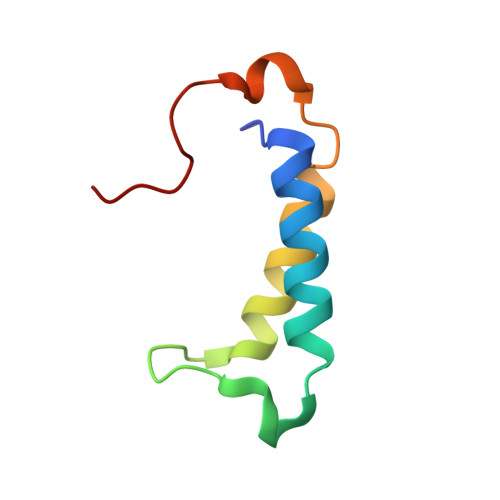
A molecular threading mechanism underlies Jumonji lysine demethylase KDM2A regulation of methylated H3K36.
Cheng, Z., Cheung, P., Kuo, A.J., Yukl, E.T., Wilmot, C.M., Gozani, O., Patel, D.J.(2014) Genes Dev 28: 1758-1771
- PubMed: 25128496
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.246561.114
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4QWN, 4QX7, 4QX8, 4QXB, 4QXC, 4QXH, 4TN7 - PubMed Abstract:
The dynamic reversible methylation of lysine residues on histone proteins is central to chromatin biology. Key components are demethylase enzymes, which remove methyl moieties from lysine residues. KDM2A, a member of the Jumonji C domain-containing histone lysine demethylase family, specifically targets lower methylation states of H3K36. Here, structural studies reveal that H3K36 specificity for KDM2A is mediated by the U-shaped threading of the H3K36 peptide through a catalytic groove within KDM2A. The side chain of methylated K36 inserts into the catalytic pocket occupied by Ni(2+) and cofactor, where it is positioned and oriented for demethylation. Key residues contributing to K36me specificity on histone H3 are G33 and G34 (positioned within a narrow channel), P38 (a turn residue), and Y41 (inserts into its own pocket). Given that KDM2A was found to also bind the H3K36me3 peptide, we postulate that steric constraints could prevent α-ketoglutarate from undergoing an "off-line"-to-"in-line" transition necessary for the demethylation reaction. Furthermore, structure-guided substitutions of residues in the KDM2A catalytic pocket abrogate KDM2A-mediated functions important for suppression of cancer cell phenotypes. Together, our results deduce insights into the molecular basis underlying KDM2A regulation of the biologically important methylated H3K36 mark.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Program, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, New York 10065, USA;