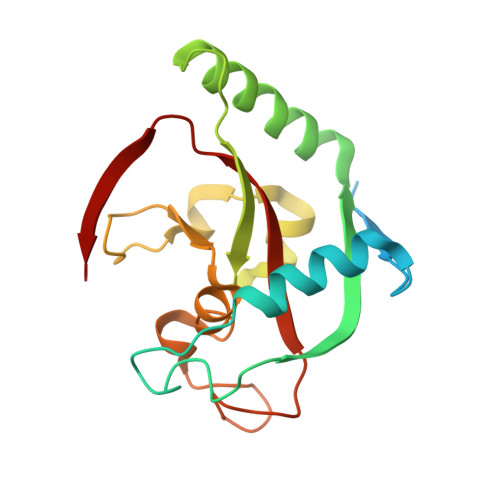
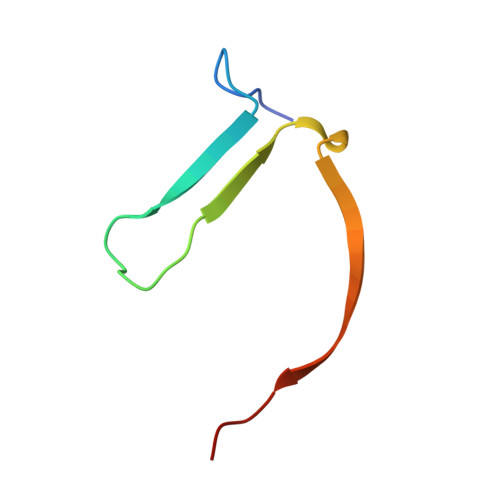
Discovery of tankyrase inhibiting flavones with increased potency and isoenzyme selectivity.
Narwal, M., Koivunen, J., Haikarainen, T., Obaji, E., Legala, O.E., Venkannagari, H., Joensuu, P., Pihlajaniemi, T., Lehtio, L.(2013) J Med Chem 56: 7880-7889
- PubMed: 24116873
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm401463y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4BS4, 4KZL, 4KZQ, 4KZU, 4L09, 4L0B, 4L0I, 4L0S, 4L0T, 4L0V, 4L10, 4L2F, 4L2G, 4L2K, 4L31, 4L32, 4L33, 4L34 - PubMed Abstract:
Tankyrases are ADP-ribosyltransferases that play key roles in various cellular pathways, including the regulation of cell proliferation, and thus, they are promising drug targets for the treatment of cancer. Flavones have been shown to inhibit tankyrases and we report here the discovery of more potent and selective flavone derivatives. Commercially available flavones with single substitutions were used for structure-activity relationship studies, and cocrystal structures of the 18 hit compounds were analyzed to explain their potency and selectivity. The most potent inhibitors were also tested in a cell-based assay, which demonstrated that they effectively antagonize Wnt signaling. To assess selectivity, they were further tested against a panel of homologous human ADP-ribosyltransferases. The most effective compound, 22 (MN-64), showed 6 nM potency against tankyrase 1, isoenzyme selectivity, and Wnt signaling inhibition. This work forms a basis for rational development of flavones as tankyrase inhibitors and guides the development of other structurally related inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Biocenter Oulu, University of Oulu , Oulu 90570, Finland.