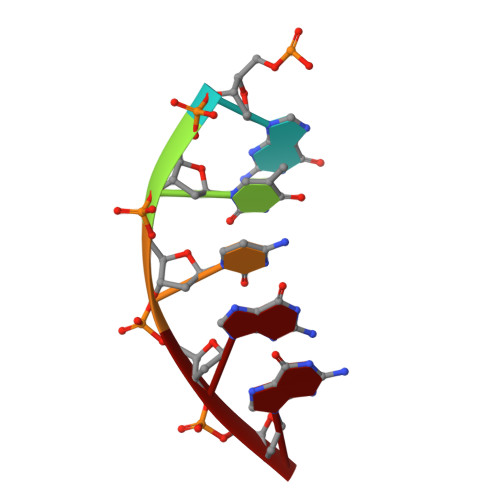
DNA polymerase minor groove interactions modulate mutagenic bypass of a templating 8-oxoguanine lesion.
Freudenthal, B.D., Beard, W.A., Wilson, S.H.(2013) Nucleic Acids Res 41: 1848-1858
- PubMed: 23267011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1276
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4GXI, 4GXJ, 4GXK - PubMed Abstract:
A major base lesion resulting from oxidative stress is 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxoG) that has ambiguous coding potential. Error-free DNA synthesis involves 8-oxoG adopting an anti-conformation to base pair with cytosine whereas mutagenic bypass involves 8-oxoG adopting a syn-conformation to base pair with adenine. Left unrepaired the syn-8-oxoG/dAMP base pair results in a G-C to T-A transversion. During base excision repair of this mispair, DNA polymerase (pol) β is confronted with gap filling opposite 8-oxoG. To determine how pol β discriminates between anti- and syn-8-oxoG, we introduced a point mutation (R283K) to alter insertion specificity. Kinetic studies demonstrate that this substitution results in an increased fidelity opposite 8-oxoG. Structural studies with R283K pol β show that the binary DNA complex has 8-oxoG in equilibrium between anti- and syn-forms. Ternary complexes with incoming dCTP resemble the wild-type enzyme, with templating anti-8-oxoG base pairing with incoming cytosine. In contrast to wild-type pol β, the ternary complex of the R283K mutant with an incoming dATP-analogue and templating 8-oxoG resembles a G-A mismatched structure with 8-oxoG adopting an anti-conformation. These results demonstrate that the incoming nucleotide is unable to induce a syn-8-oxoG conformation without minor groove DNA polymerase interactions that influence templating (anti-/syn-equilibrium) of 8-oxoG while modulating fidelity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Structural Biology, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, NIH, PO Box 12233, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709-2233, USA.