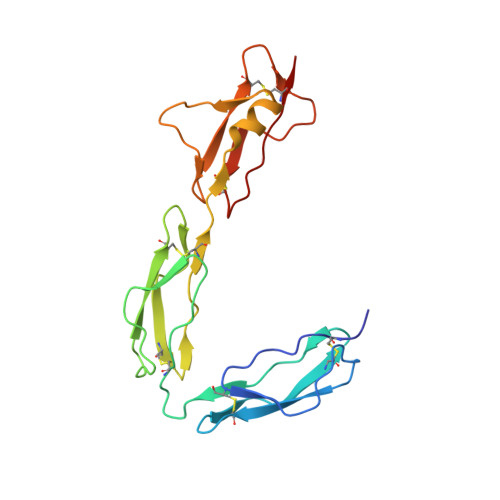
Structural Analysis of the C-Terminal Region (Modules 18-20) of Complement Regulator Factor H (FH).
Morgan, H.P., Mertens, H.D., Guariento, M., Schmidt, C.Q., Soares, D.C., Svergun, D.I., Herbert, A.P., Barlow, P.N., Hannan, J.P.(2012) PLoS One 7: e32187-e32187
- PubMed: 22389686
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0032187
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3SW0 - PubMed Abstract:
Factor H (FH) is a soluble regulator of the human complement system affording protection to host tissues. It selectively inhibits amplification of C3b, the activation-specific fragment of the abundant complement component C3, in fluid phase and on self-surfaces and accelerates the decay of the alternative pathway C3 convertase, C3bBb. We have determined the crystal structure of the three carboxyl-terminal complement control protein (CCP) modules of FH (FH18-20) that bind to C3b, and which additionally recognize polyanionic markers specific to self-surfaces. These CCPs harbour nearly 30 disease-linked missense mutations. We have also deployed small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) to investigate FH18-20 flexibility in solution using FH18-20 and FH19-20 constructs. In the crystal lattice FH18-20 adopts a "J"-shape: A ~122-degree tilt between the structurally highly similar modules 18 and 19 precedes an extended, linear arrangement of modules 19 and 20 as observed in previously determined structures of these two modules alone. However, under solution conditions FH18-20 adopts multiple conformations mediated by flexibility between CCPs 18 and 19. We also pinpoint the locations of disease-associated missense mutations on the module 18 surface and discuss our data in the context of the C3b:FH interaction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Structural and Molecular Biology, School of Biological Sciences, King's Buildings, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom.