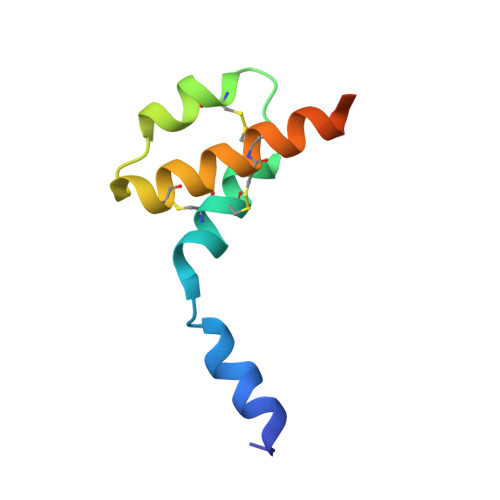
Structure of human desArg-C5a.
Cook, W.J., Galakatos, N., Boyar, W.C., Walter, R.L., Ealick, S.E.(2010) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 66: 190-197
- PubMed: 20124699
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444909049051
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3HQA, 3HQB - PubMed Abstract:
The anaphylatoxin C5a is derived from the complement component C5 during activation of the complement cascade. It is an important component in the pathogenesis of a number of inflammatory diseases. NMR structures of human and porcine C5a have been reported; these revealed a four-helix bundle stabilized by three disulfide bonds. The crystal structure of human desArg-C5a has now been determined in two crystal forms. Surprisingly, the protein crystallizes as a dimer and each monomer in the dimer has a three-helix core instead of the four-helix bundle noted in the NMR structure determinations. Furthermore, the N-terminal helices of the two monomers occupy different positions relative to the three-helix core and are completely different from the NMR structures. The physiological significance of these structural differences is unknown.
Organizational Affiliation:
University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL 35294, USA. wjcook@uab.edu