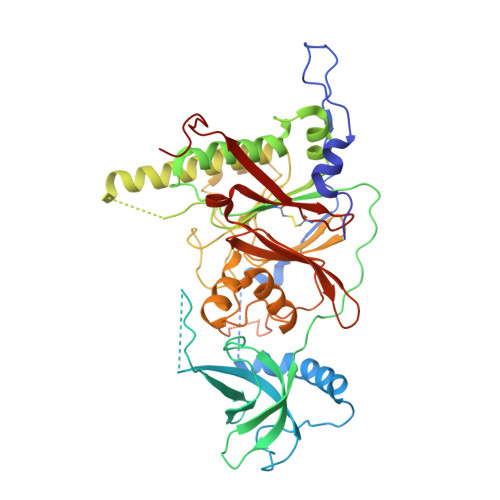
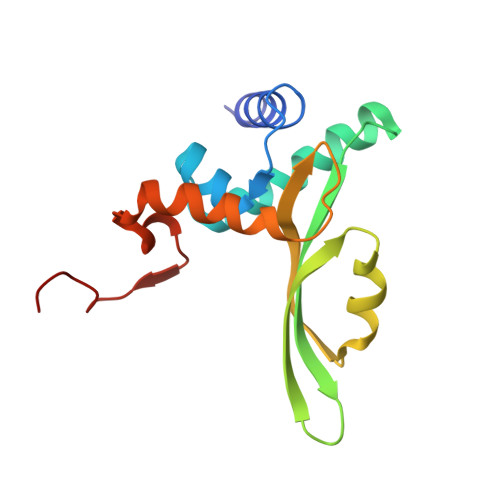
X-ray structure of the complex of regulatory subunits of human DNA polymerase delta.
Baranovskiy, A.G., Babayeva, N.D., Liston, V.G., Rogozin, I.B., Koonin, E.V., Pavlov, Y.I., Vassylyev, D.G., Tahirov, T.H.(2008) Cell Cycle 7: 3026-3036
- PubMed: 18818516
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.7.19.6720
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3E0J - PubMed Abstract:
The eukaryotic DNA polymerase delta (Pol delta) participates in genome replication, homologous recombination, DNA repair and damage tolerance. Regulation of the plethora of Pol delta functions depends on the interaction between the second (p50) and third (p66) non-catalytic subunits. We report the crystal structure of p50*p66(N) complex featuring oligonucleotide binding and phosphodiesterase domains in p50 and winged helix-turn-helix N-terminal domain in p66. Disruption of the interaction between the yeast orthologs of p50 and p66 by strategic amino acid changes leads to cold-sensitivity, sensitivity to hydroxyurea and to reduced UV mutagenesis, mimicking the phenotypes of strains where the third subunit of Pol delta is absent. The second subunits of all B family replicative DNA polymerases in archaea and eukaryotes, except Pol delta, share a three-domain structure similar to p50*p66(N), raising the possibility that a portion of the gene encoding p66 was derived from the second subunit gene relatively late in evolution.
Organizational Affiliation:
Eppley Institute for Research in Cancer and Allied Diseases, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, Nebraska 68198-7696, USA.