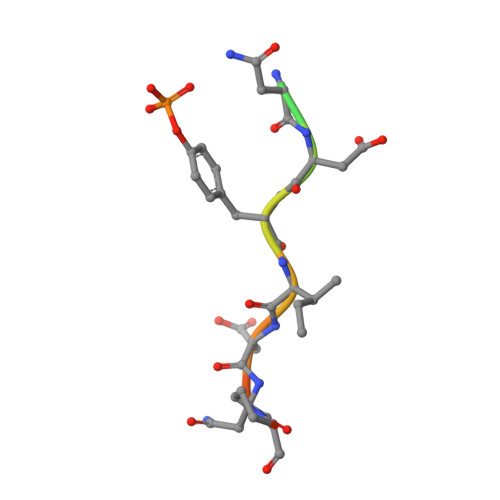
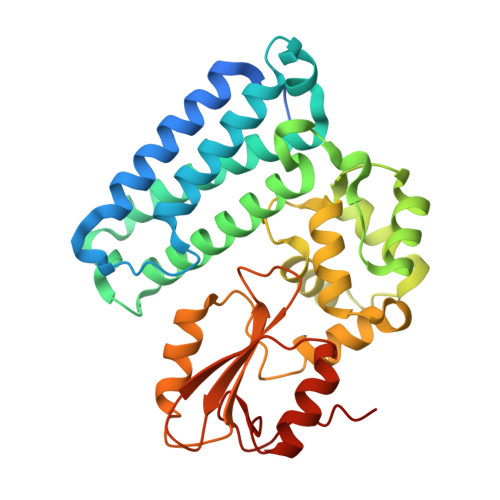
Structural basis for a novel intrapeptidyl H-bond and reverse binding of c-Cbl-TKB domain substrates
Ng, C., Jackson, R.A., Buschdorf, J.P., Sun, Q., Guy, G.R., Sivaraman, J.(2008) EMBO J 27: 804-816
- PubMed: 18273061
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2008.18
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3BUM, 3BUN, 3BUO, 3BUW, 3BUX - PubMed Abstract:
The c-Cbl tyrosine kinase binding domain (Cbl-TKB), essentially an 'embedded' SH2 domain, has a critical role in targeting proteins for ubiquitination. To address how this domain can bind to disparate recognition mofits and to determine whether this results in variations in substrate-binding affinity, we compared crystal structures of the Cbl-TKB domain complexed with phosphorylated peptides of Sprouty2, Sprouty4, epidermal growth factor receptor, Syk, and c-Met receptors and validated the binding with point-mutational analyses using full-length proteins. An obligatory, intrapeptidyl H-bond between the phosphotyrosine and the conserved asparagine or adjacent arginine is essential for binding and orients the peptide into a positively charged pocket on c-Cbl. Surprisingly, c-Met bound to Cbl in the reverse direction, which is unprecedented for SH2 domain binding. The necessity of this intrapeptidyl H-bond was confirmed with isothermal titration calorimetry experiments that also showed Sprouty2 to have the highest binding affinity to c-Cbl; this may enable the selective sequestration of c-Cbl from other target proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, National University of Singapore, Singapore.