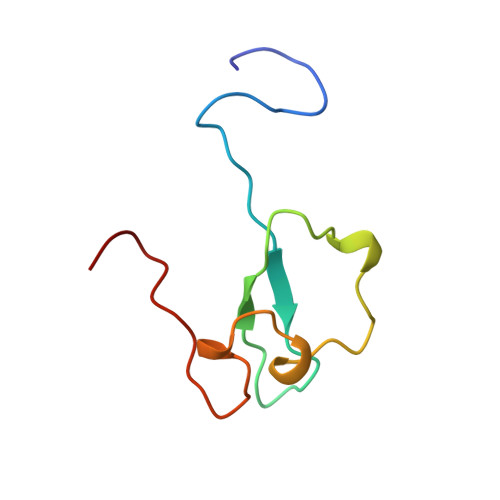
Structural insight into the zinc finger CW domain as a histone modification reader
He, F., Umehara, T., Saito, K., Harada, T., Watanabe, S., Yabuki, T., Kigawa, T., Takahashi, M., Kuwasako, K., Tsuda, K., Matsuda, T., Aoki, M., Seki, E., Kobayashi, N., Guntert, P., Yokoyama, S., Muto, Y.(2010) Structure 18: 1127-1139
- PubMed: 20826339
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2010.06.012
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2E61, 2RR4 - PubMed Abstract:
The zinc finger CW (zf-CW) domain is a motif of about 60 residues that is frequently found in proteins involved in epigenetic regulation. Here, we determined the NMR solution structure of the zf-CW domain of the human zf-CW and PWWP domain containing protein 1 (ZCWPW1). The zf-CW domain adopts a new fold in which a zinc ion is coordinated tetrahedrally by four conserved Cys ligand residues. The tertiary structure of the zf-CW domain partially resembles that adopted by the plant homeo domain (PHD) finger bound to the histone tail, suggesting that the zf-CW domain and the PHD finger have similar functions. The solution structure of the complex of the zf-CW domain with the histone H3 tail peptide (1-10) with trimethylated K4 clarified its binding mode. Our structural and biochemical studies have identified the zf-CW domain as a member of the histone modification reader modules for epigenetic regulation.
Organizational Affiliation:
RIKEN Systems and Structural Biology Center, 1-7-22 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi-ku, Yokohama 230-0045, Japan.