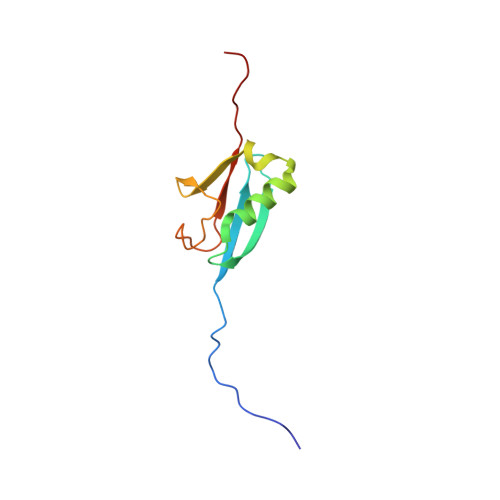
Molecular Basis for Phosphorylation-dependent SUMO Recognition by the DNA Repair Protein RAP80.
Anamika, Spyracopoulos, L.(2016) J Biol Chem 291: 4417-4428
- PubMed: 26719330
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.705061
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2N9E - PubMed Abstract:
Recognition and repair of double-stranded DNA breaks (DSB) involves the targeted recruitment of BRCA tumor suppressors to damage foci through binding of both ubiquitin (Ub) and the Ub-like modifier SUMO. RAP80 is a component of the BRCA1 A complex, and plays a key role in the recruitment process through the binding of Lys(63)-linked poly-Ub chains by tandem Ub interacting motifs (UIM). RAP80 also contains a SUMO interacting motif (SIM) just upstream of the tandem UIMs that has been shown to specifically bind the SUMO-2 isoform. The RAP80 tandem UIMs and SIM function collectively for optimal recruitment of BRCA1 to DSBs, although the molecular basis of this process is not well understood. Using NMR spectroscopy, we demonstrate that the RAP80 SIM binds SUMO-2, and that both specificity and affinity are enhanced through phosphorylation of the canonical CK2 site within the SIM. The affinity increase results from an enhancement of electrostatic interactions between the phosphoserines of RAP80 and the SIM recognition module within SUMO-2. The NMR structure of the SUMO-2·phospho-RAP80 complex reveals that the molecular basis for SUMO-2 specificity is due to isoform-specific sequence differences in electrostatic SIM recognition modules.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Department of Biochemistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta T6G 2H7, Canada.