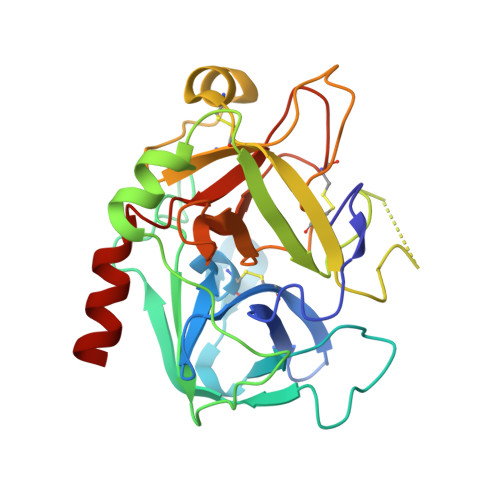
Crystal structure of thrombin in complex with fibrinogen gamma' peptide.
Pineda, A.O., Chen, Z.W., Marino, F., Mathews, F.S., Mosesson, M.W., Di Cera, E.(2007) Biophys Chem 125: 556-559
- PubMed: 16962697
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpc.2006.08.005
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2HWL - PubMed Abstract:
Elevated levels of heterodimeric gamma(A)/gamma' fibrinogen 2 have been associated with an increased incidence of coronary artery disease, whereas a lowered content of gamma' chains is associated with an increased risk of venous thrombosis. Both situations may be related to the unique features of thrombin binding to variant gamma' chains. The gamma' peptide is an anionic fragment that binds thrombin with high affinity without interfering directly with substrate binding. Here we report the crystal structure of thrombin bound to the gamma' peptide, solved at 2.4 A resolution. The complex reveals extensive interactions between thrombin and the gamma' peptide mediated by electrostatic contacts with residues of exosite II and hydrophobic interactions with a pocket in close proximity to the Na(+) binding site. In its binding mode, the gamma' peptide completely overlaps with heparin bound to exosite II. These findings are consistent with functional data and broaden our understanding of how thrombin interacts with fibrinogen at the molecular level.