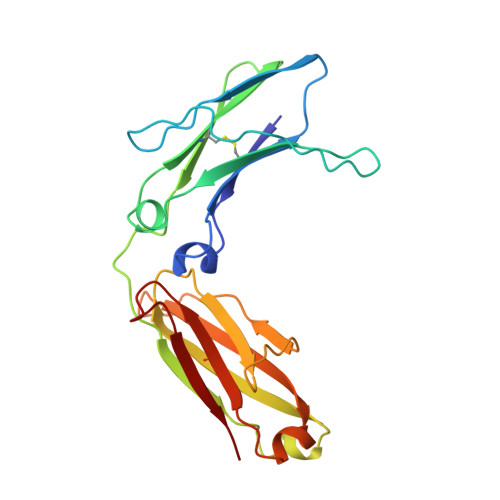
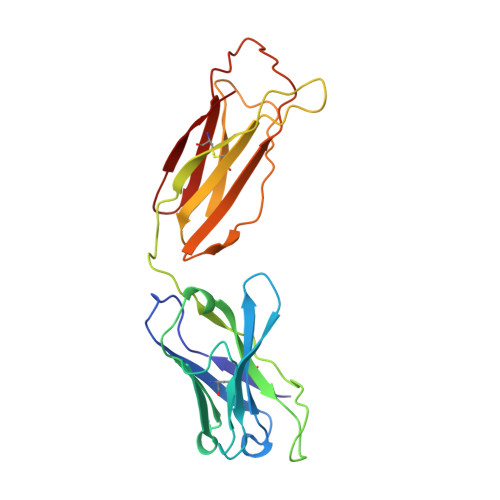
Structure of human IgM rheumatoid factor Fab bound to its autoantigen IgG Fc reveals a novel topology of antibody-antigen interaction.
Corper, A.L., Sohi, M.K., Bonagura, V.R., Steinitz, M., Jefferis, R., Feinstein, A., Beale, D., Taussig, M.J., Sutton, B.J.(1997) Nat Struct Biol 4: 374-381
- PubMed: 9145108
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0597-374
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ADQ - PubMed Abstract:
Rheumatoid factors are the characteristic autoantibodies of rheumatoid arthritis, which bind to the Fc regions of IgG molecules. Here we report the crystal structure of the Fab fragment of a patient-derived IgM rheumatoid factor (RF-AN) complexed with human IgG4 Fc, at 3.2 A resolution. This is the first structure of an autoantibody-autoantigen complex. The epitope recognised in IgG Fc includes the C gamma 2/C gamma 3 cleft region, and overlaps the binding sites of bacterial Fc-binding proteins. The antibody residues involved in autorecognition are all located at the edge of the conventional combining site surface, leaving much of the latter available, potentially, for recognition of a different antigen. Since an important contact residue is somatic mutation, the structure implicates antigen-driven selection, following somatic mutation of germline genes, in the production of pathogenic rheumatoid factors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Randall Institute, King's College London, UK.