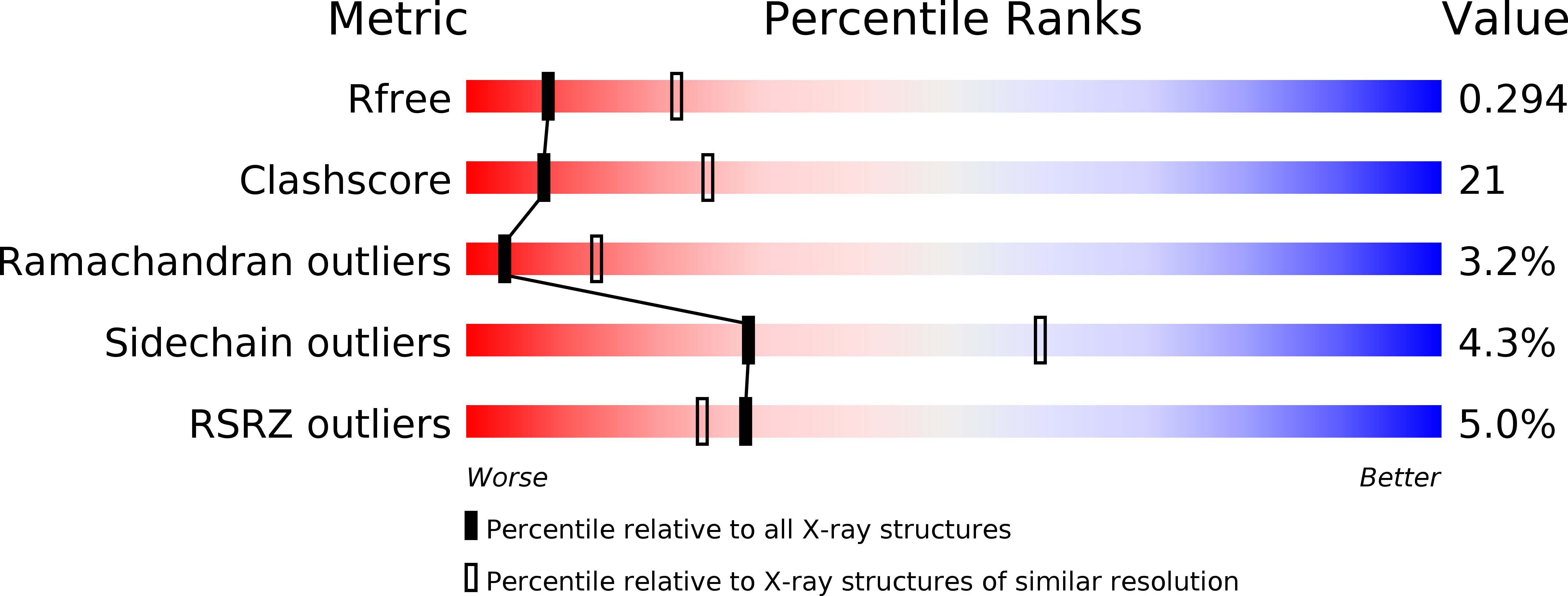
Crystal structure of the homologous-pairing domain from the human Rad52 recombinase in the undecameric form.
Kagawa, W., Kurumizaka, H., Ishitani, R., Fukai, S., Nureki, O., Shibata, T., Yokoyama, S.(2002) Mol Cell 10: 359-371
- PubMed: 12191481
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00587-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1KN0 - PubMed Abstract:
The human Rad52 protein forms a heptameric ring that catalyzes homologous pairing. The N-terminal half of Rad52 is the catalytic domain for homologous pairing, and the ring formed by the domain fragment was reported to be approximately decameric. Splicing variants of Rad52 and a yeast homolog (Rad59) are composed mostly of this domain. In this study, we determined the crystal structure of the homologous-pairing domain of human Rad52 and revealed that the domain forms an undecameric ring. Each monomer has a beta-beta-beta-alpha fold, which consists of highly conserved amino acid residues among Rad52 homologs. A mutational analysis revealed that the amino acid residues located between the beta-beta-beta-alpha fold and the characteristic hairpin loop are essential for ssDNA and dsDNA binding.
Organizational Affiliation:
RIKEN Genomic Sciences Center, 1-7-22 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi, Yokohama, Japan.