Identification and evaluation of potential inhibitor molecules against TcyA from Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus.
Lonare, S., Sharma, M., Dalal, V., Gubyad, M., Kumar, P., Nath Gupta, D., Pareek, A., Tomar, S., Kumar Ghosh, D., Kumar, P., Kumar Sharma, A.(2023) J Struct Biol 215: 107992-107992
- PubMed: 37394197
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2023.107992
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8GTU, 8GU1 - PubMed Abstract:
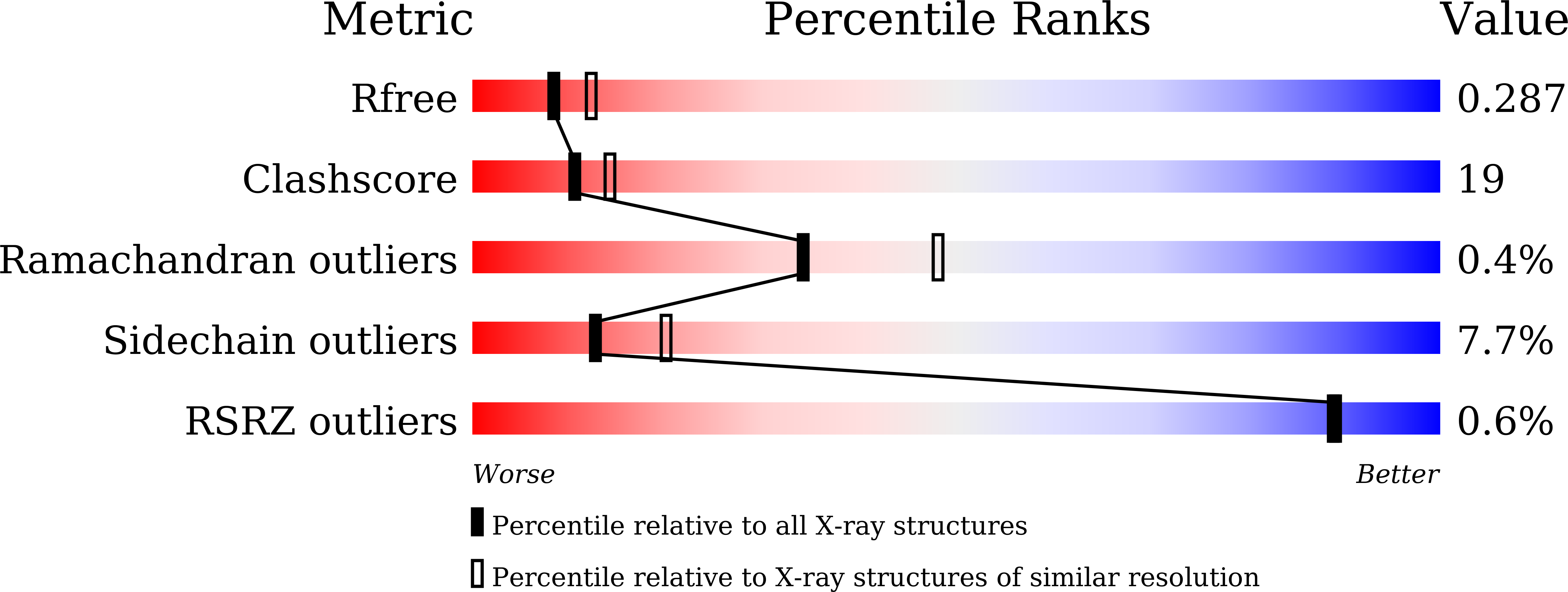
Of the two putative amino acid binding periplasmic receptors of ABC transporter family in Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus (CLas), cystine binding receptor (CLasTcyA) has been shown to mainly express in phloem of citrus plant and is a target for inhibitor development. The crystal structure of CLasTcyA in complex with substrates has been reported earlier. The present work reports the identification and evaluation of potential candidates for their inhibitory potential against CLasTcyA. Among many compounds, selected through virtual screening, and MD simulation, pimozide, clidinium, sulfasalazine and folic acid showed significantly higher affinities and stability in complex with CLasTcyA. The SPR studies with CLasTcyA revealed significantly higher binding affinities for pimozide and clidinium (Kd, 2.73 nM and 70 nM, respectively) as compared to cystine (Kd, 1.26 µM). The higher binding affinities could be attributed to significantly increased number of interactions in the binding pocket as evident from the crystal structures of CLasTcyA in complex with pimozide and clidinium as compared to cystine. The CLasTcyA possess relatively large binding pocket where bulkier inhibitors fit quite well. In planta studies, carried out to assess the effect of inhibitors on HLB infected Mosambi plants, showed significant reduction in CLas titre in plants treated with inhibitors as compared to control plants. The results showed that pimozide exhibited higher efficiency as compared to clidinium in reducing CLas titre in treated plants. Our results showed that the inhibitor development against critical proteins like CLasTcyA can be an important strategy in management of HLB.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee-247667, India.