High-throughput structure determination of an intrinsically disordered protein using cell-free protein crystallization.
Kojima, M., Abe, S., Furuta, T., Hirata, K., Yao, X., Kobayashi, A., Kobayashi, R., Ueno, T.(2024) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 121: e2322452121-e2322452121
- PubMed: 38861600
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2322452121
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8J2Q, 8WLG, 8X8S, 8X8V - PubMed Abstract:
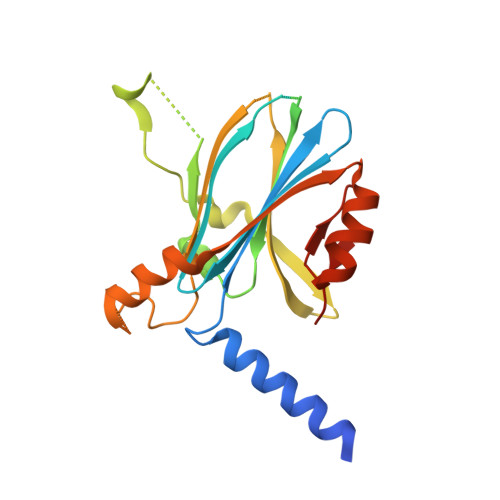
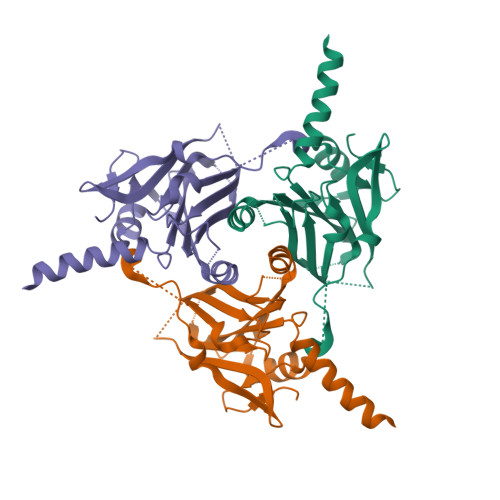
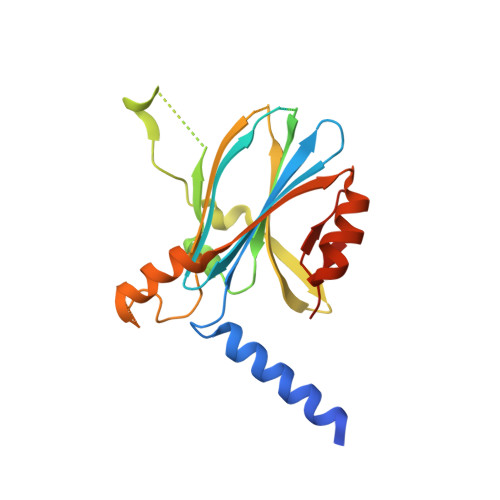
Intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) play a crucial role in various biological phenomena, dynamically changing their conformations in response to external environmental cues. To gain a deeper understanding of these proteins, it is essential to identify the determinants that fix their structures at the atomic level. Here, we developed a pipeline for rapid crystal structure analysis of IDP using a cell-free protein crystallization (CFPC) method. Through this approach, we successfully demonstrated the determination of the structure of an IDP to uncover the key determinants that stabilize its conformation. Specifically, we focused on the 11-residue fragment of c-Myc, which forms an α-helix through dimerization with a binding partner protein. This fragment was strategically recombined with an in-cell crystallizing protein and was expressed in a cell-free system. The resulting crystal structures of the c-Myc fragment were successfully determined at a resolution of 1.92 Å and we confirmed that they are identical to the structures of the complex with the native binding partner protein. This indicates that the environment of the scaffold crystal can fix the structure of c-Myc. Significantly, these crystals were obtained directly from a small reaction mixture (30 µL) incubated for only 72 h. Analysis of eight crystal structures derived from 22 mutants revealed two hydrophobic residues as the key determinants responsible for stabilizing the α-helical structure. These findings underscore the power of our CFPC screening method as a valuable tool for determining the structures of challenging target proteins and elucidating the essential molecular interactions that govern their stability.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Life Science and Technology, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501, Japan.