Mechanistic insights into intramembrane proteolysis by E. coli site-2 protease homolog RseP.
Imaizumi, Y., Takanuki, K., Miyake, T., Takemoto, M., Hirata, K., Hirose, M., Oi, R., Kobayashi, T., Miyoshi, K., Aruga, R., Yokoyama, T., Katagiri, S., Matsuura, H., Iwasaki, K., Kato, T., Kaneko, M.K., Kato, Y., Tajiri, M., Akashi, S., Nureki, O., Hizukuri, Y., Akiyama, Y., Nogi, T.(2022) Sci Adv 8: eabp9011-eabp9011
- PubMed: 36001659
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abp9011
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7W6X, 7W6Y, 7W6Z, 7W70, 7W71 - PubMed Abstract:
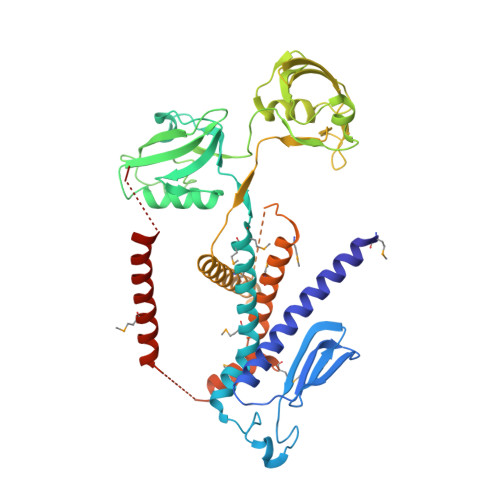
Site-2 proteases are a conserved family of intramembrane proteases that cleave transmembrane substrates to regulate signal transduction and maintain proteostasis. Here, we elucidated crystal structures of inhibitor-bound forms of bacterial site-2 proteases including Escherichia coli RseP. Structure-based chemical modification and cross-linking experiments indicated that the RseP domains surrounding the active center undergo conformational changes to expose the substrate-binding site, suggesting that RseP has a gating mechanism to regulate substrate entry. Furthermore, mutational analysis suggests that a conserved electrostatic linkage between the transmembrane and peripheral membrane-associated domains mediates the conformational changes. In vivo cleavage assays also support that the substrate transmembrane helix is unwound by strand addition to the intramembrane β sheet of RseP and is clamped by a conserved asparagine residue at the active center for efficient cleavage. This mechanism underlying the substrate binding, i.e., unwinding and clamping, appears common across distinct families of intramembrane proteases that cleave transmembrane segments.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Medical Life Science, Yokohama City University, 1-7-29 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi-ku, Yokohama 230-0045, Japan.