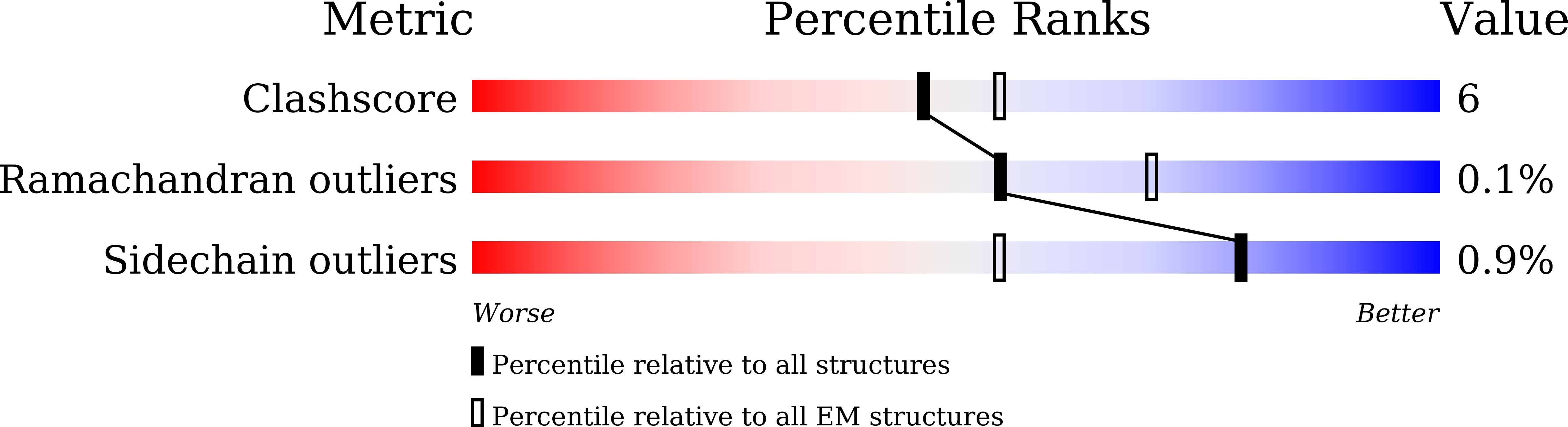Cryo-EM structure of the human MT 1 -G i signaling complex.
Okamoto, H.H., Miyauchi, H., Inoue, A., Raimondi, F., Tsujimoto, H., Kusakizako, T., Shihoya, W., Yamashita, K., Suno, R., Nomura, N., Kobayashi, T., Iwata, S., Nishizawa, T., Nureki, O.(2021) Nat Struct Mol Biol 28: 694-701
- PubMed: 34354246
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-021-00634-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7DB6 - PubMed Abstract:
Melatonin receptors (MT 1 and MT 2 ) transduce inhibitory signaling by melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine), which is associated with sleep induction and circadian rhythm modulation. Although recently reported crystal structures of ligand-bound MT 1 and MT 2 elucidated the basis of ligand entry and recognition, the ligand-induced MT 1 rearrangement leading to G i -coupling remains unclear. Here we report a cryo-EM structure of the human MT 1 -G i signaling complex at 3.3 Å resolution, revealing melatonin-induced conformational changes propagated to the G-protein-coupling interface during activation. In contrast to other G i -coupled receptors, MT 1 exhibits a large outward movement of TM6, which is considered a specific feature of G s -coupled receptors. Structural comparison of G i and G s complexes demonstrated conformational diversity of the C-terminal entry of the G i protein, suggesting loose and variable interactions at the end of the α5 helix of G i protein. These notions, together with our biochemical and computational analyses, highlight variable binding modes of Gα i and provide the basis for the selectivity of G-protein signaling.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan.