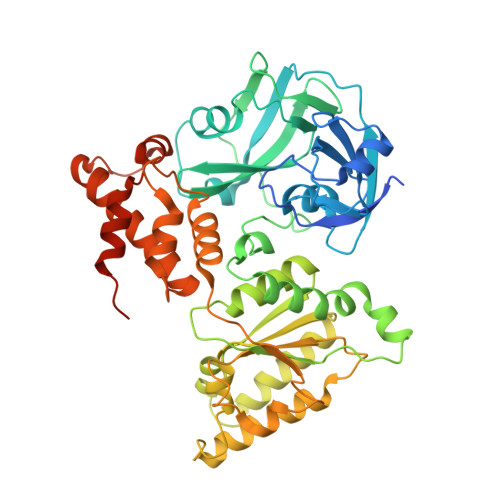
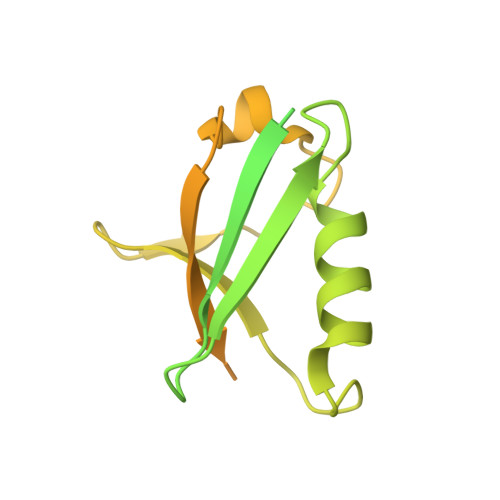
Common Mode of Remodeling AAA ATPases p97/CDC48 by Their Disassembling Cofactors ASPL/PUX1.
Banchenko, S., Arumughan, A., Petrovic, S., Schwefel, D., Wanker, E.E., Roske, Y., Heinemann, U.(2019) Structure 27: 1830
- PubMed: 31648844
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2019.10.001
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6HD0, 6HD3 - PubMed Abstract:
The hexameric ring structure of the type II AAA+ ATPases is considered as stable and permanent. Recently, the UBX domain-containing cofactors Arabidopsis thaliana PUX1 and human alveolar soft part sarcoma locus (ASPL) were reported to bind and disassemble the cognate AAA+ ATPases AtCDC48 and human p97. Here, we present two crystal structures related to these complexes: a truncated AtCDC48 (AtCDC48-ND1) and a hybrid complex containing human p97-ND1 and the UBX domain of plant PUX1 (p97-ND1:PUX1-UBX). These structures reveal close similarity between the human and plant AAA+ ATPases, but also highlight differences between disassembling and non-disassembling AAA+ ATPase cofactors. Based on an AtCDC48 disassembly assay with PUX1 and known crystal structures of the p97-bound human cofactor ASPL, we propose a general ATPase disassembly model. Thus, our structural and biophysical investigations provide detailed insight into the mechanism of AAA+ ATPase disassembly by UBX domain cofactors and suggest a general mode of regulating the cellular activity of these molecular machines.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max-Delbrück-Centrum für Molekulare Medizin, 13125 Berlin, Germany; Institut für Chemie und Biochemie, Freie Universität Berlin, 14195 Berlin, Germany.