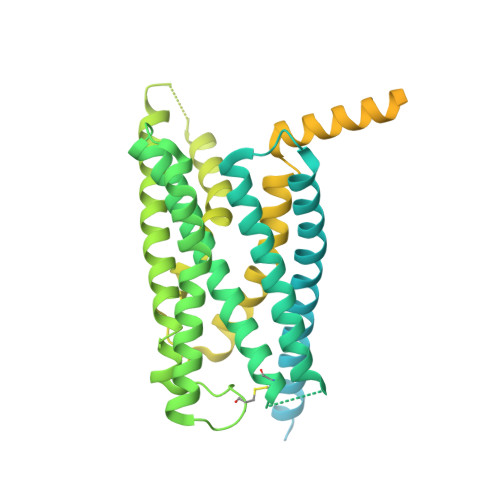
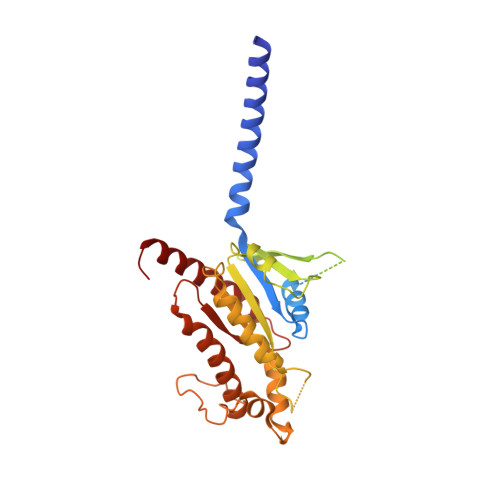
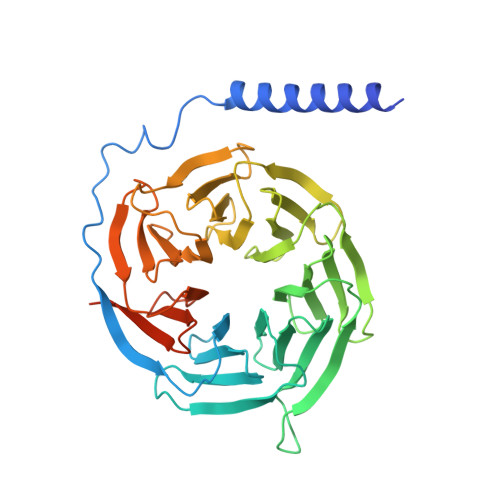
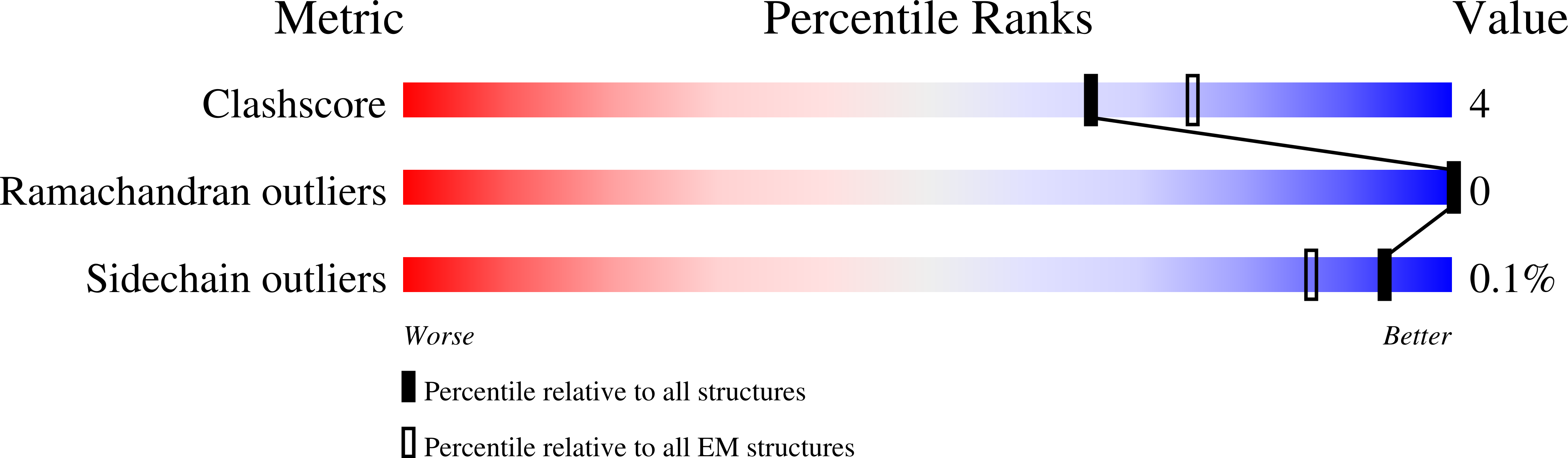Cryo-EM structure of an activated VIP1 receptor-G protein complex revealed by a NanoBiT tethering strategy.
Duan, J., Shen, D.D., Zhou, X.E., Bi, P., Liu, Q.F., Tan, Y.X., Zhuang, Y.W., Zhang, H.B., Xu, P.Y., Huang, S.J., Ma, S.S., He, X.H., Melcher, K., Zhang, Y., Xu, H.E., Jiang, Y.(2020) Nat Commun 11: 4121-4121
- PubMed: 32807782
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-17933-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6VN7 - PubMed Abstract:
Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptor (VIP1R) is a widely expressed class B G protein-coupled receptor and a drug target for the treatment of neuronal, metabolic, and inflammatory diseases. However, our understanding of its mechanism of action and the potential of drug discovery targeting this receptor is limited by the lack of structural information of VIP1R. Here we report a cryo-electron microscopy structure of human VIP1R bound to PACAP27 and Gs heterotrimer, whose complex assembly is stabilized by a NanoBiT tethering strategy. Comparison with other class B GPCR structures reveals that PACAP27 engages VIP1R with its N-terminus inserting into the ligand binding pocket at the transmembrane bundle of the receptor, which subsequently couples to the G protein in a receptor-specific manner. This structure has provided insights into the molecular basis of PACAP27 binding and VIP receptor activation. The methodology of the NanoBiT tethering may help to provide structural information of unstable complexes.
Organizational Affiliation:
The CAS Key Laboratory of Receptor Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 201203, China.