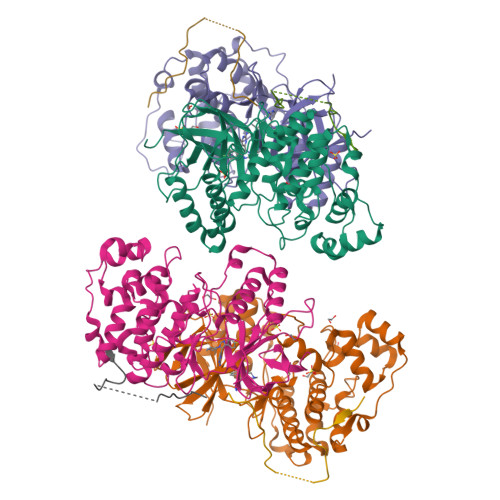
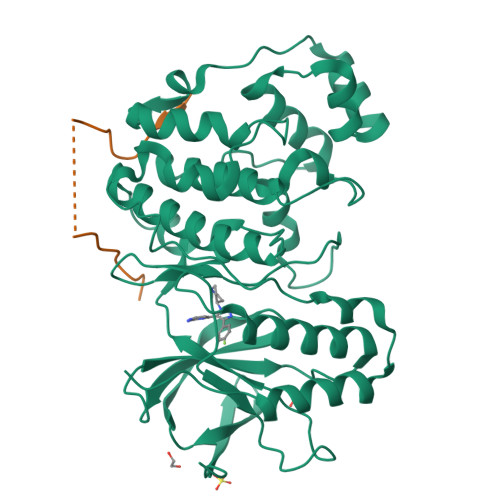
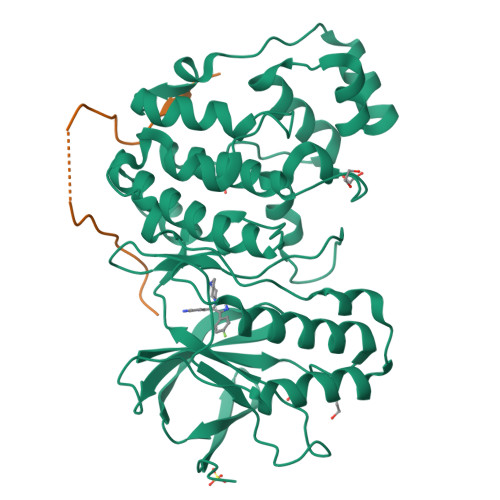
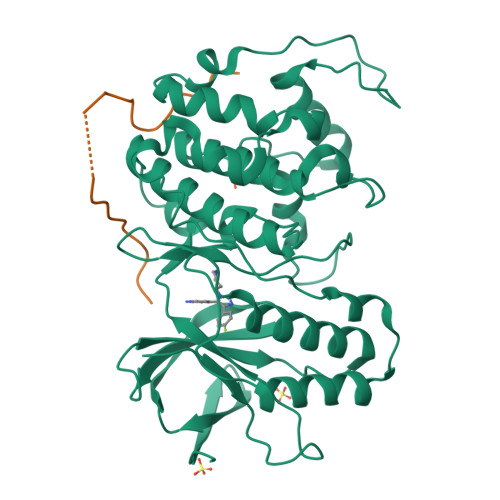
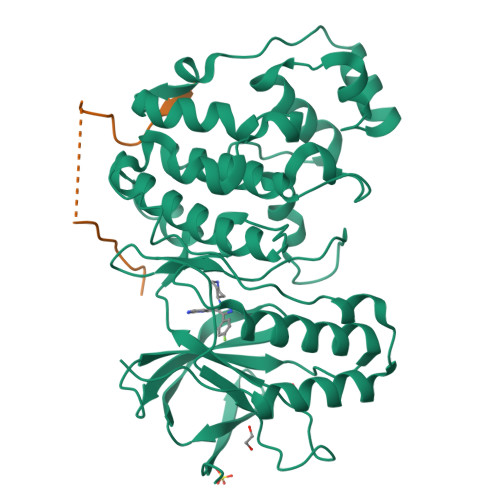
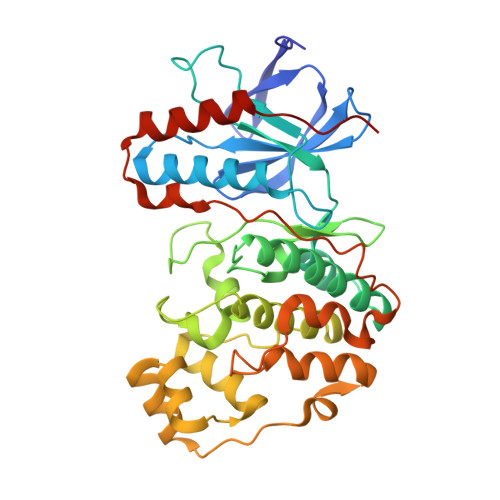
Mechanism and consequence of the autoactivation of p38 alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase promoted by TAB1.
De Nicola, G.F., Martin, E.D., Chaikuad, A., Bassi, R., Clark, J., Martino, L., Verma, S., Sicard, P., Tata, R., Atkinson, R.A., Knapp, S., Conte, M.R., Marber, M.S.(2013) Nat Struct Mol Biol 20: 1182-1190
- PubMed: 24037507
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2668
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4LOO, 4LOP, 4LOQ - PubMed Abstract:
p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38α) is activated by a variety of mechanisms, including autophosphorylation initiated by TGFβ-activated kinase 1 binding protein 1 (TAB1) during myocardial ischemia and other stresses. Chemical-genetic approaches and coexpression in mammalian, bacterial and cell-free systems revealed that mouse p38α autophosphorylation occurs in cis by direct interaction with TAB1(371-416). In isolated rat cardiac myocytes and perfused mouse hearts, TAT-TAB1(371-416) rapidly activates p38 and profoundly perturbs function. Crystal structures and characterization in solution revealed a bipartite docking site for TAB1 in the p38α C-terminal kinase lobe. TAB1 binding stabilizes active p38α and induces rearrangements within the activation segment by helical extension of the Thr-Gly-Tyr motif, allowing autophosphorylation in cis. Interference with p38α recognition by TAB1 abolishes its cardiac toxicity. Such intervention could potentially circumvent the drawbacks of clinical pharmacological inhibitors of p38 catalytic activity.
Organizational Affiliation:
King's College London British Heart Foundation Centre of Excellence. The Rayne Institute, St Thomas' Hospital Campus, London, SE1 7EH, UK.