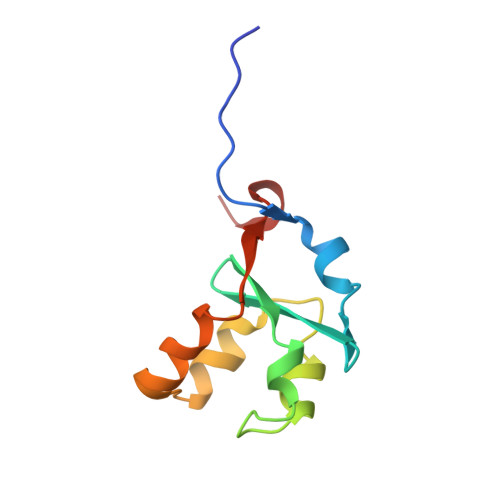
Accommodating a Non-Conservative Internal Mutation by Water-Mediated Hydrogen-Bonding Between beta-Sheet Strands: A Comparison of Human and Rat Type B (Mitochondrial) Cytochrome b5
Parthasarathy, S., Altuve, A., Terzyan, S., Zhang, X., Kuczera, K., Rivera, M., Benson, D.R.(2011) Biochemistry 50: 5544-5554
- PubMed: 21574570
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi2004729
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3MUS, 3NER - PubMed Abstract:
Mammalian type B (mitochondrial) b(5) cytochromes exhibit greater amino acid sequence diversity than their type A (microsomal) counterparts, as exemplified by the type B proteins from human (hCYB5B) and rat (rCYB5B). The comparison of X-ray crystal structures of hCYB5B and rCYB5B reported herein reveals a striking difference in packing involving the five-strand β-sheet, which can be attributed to fully buried residue 21 in strand β4. The greater bulk of Leu21 in hCYB5B in comparison to that of Thr21 in rCYB5B results in a substantial displacement of the first two residues in β5, and consequent loss of two of the three hydrogen bonds between β5 and β4. Hydrogen bonding between the residues is instead mediated by two well-ordered, fully buried water molecules. In a 10 ns molecular dynamics simulation, one of the buried water molecules in the hCYB5B structure exchanged readily with solvent via intermediates having three water molecules sandwiched between β4 and β5. When the buried water molecules were removed prior to a second 10 ns simulation, β4 and β5 formed persistent hydrogen bonds identical to those in rCYB5B, but the Leu21 side chain was forced to adopt a rarely observed conformation. Despite the apparently greater ease of access of water to the interior of hCYB5B than of rCYB5B suggested by these observations, the two proteins exhibit virtually identical stability, dynamic, and redox properties. The results provide new insight into the factors stabilizing the cytochrome b(5) fold.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biosciences, University of Kansas, Lawrence, Kansas 66045, USA.