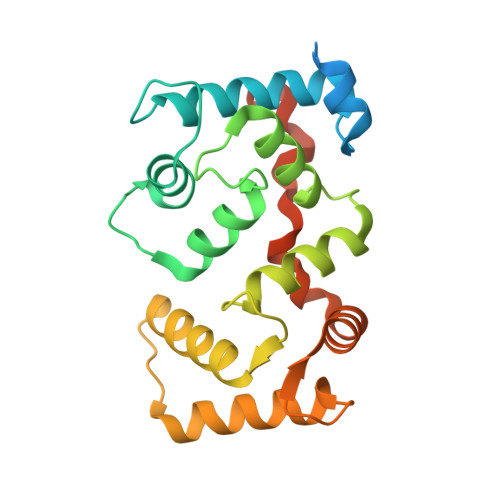
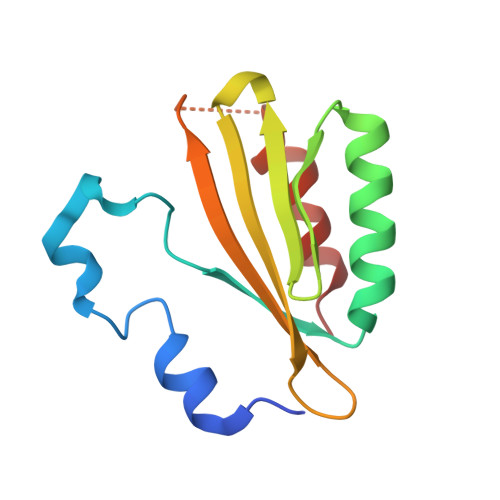
The crystal structure of plant-specific calcium-binding protein AtCBL2 in complex with the regulatory domain of AtCIPK14
Akaboshi, M., Hashimoto, H., Ishida, H., Saijo, S., Koizumi, N., Sato, M., Shimizu, T.(2008) J Mol Biol 377: 246-257
- PubMed: 18237745
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.01.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2ZFD - PubMed Abstract:
Calcium signals mediate a multitude of plant responses to external stimuli. Calcineurin B-like (CBL) proteins and their target kinases, CBL-interacting protein kinases (CIPKs), represent important relays in plant calcium signaling. CBL interacts with CIPK through a conserved motif (NAF/FISL motif) within the C-terminal regulatory domain. To better understand the functional role of the CBL-CIPK system, we determined the crystal structure of AtCBL2 in complex with the regulatory domain of AtCIPK14 at 1.2 A resolution. The NAF/FISL motif is inserted into a hydrophobic crevice within AtCBL2, accompanied by a large displacement of the helices and loop on the opposite side of the NAF/FISL motif from the C-terminal region, which shields the hydrophobic crevice in free form. Ca(2+) are coordinated within four EF hands in AtCBL2 in bound form. This calcium coordination pattern differs from that in the structure of the SOS3-SOS2 complex previously reported. Structural comparison of the two structures shows that the recognition of CBL by CIPK is performed in a similar manner, but inherent interactions confer binding affinity and specificity.
Organizational Affiliation:
International Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, Yokohama City University, 1-7-29 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi-ku, Yokohama, Kanagawa 230-0045, Japan.