Structural and functional characterization of transmembrane segment IV of the NHE1 isoform of the Na+/H+ exchanger.
Slepkov, E.R., Rainey, J.K., Li, X., Liu, Y., Cheng, F.J., Lindhout, D.A., Sykes, B.D., Fliegel, L.(2005) J Biol Chem 280: 17863-17872
- PubMed: 15677483
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M409608200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1Y4E - PubMed Abstract:
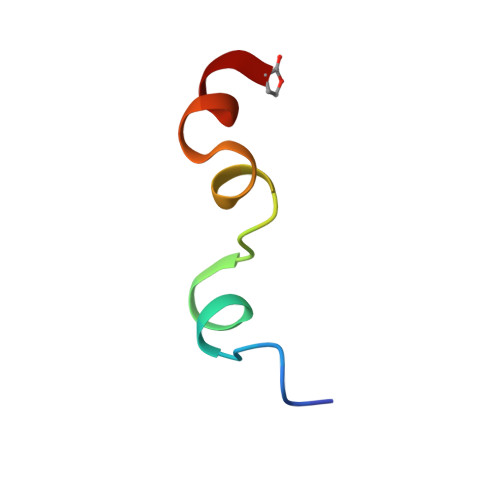
The Na(+)/H(+) exchanger isoform 1 is a ubiquitously expressed integral membrane protein that regulates intracellular pH in mammals. We characterized the structural and functional aspects of the critical transmembrane (TM) segment IV. Each residue was mutated to cysteine in cysteine-less NHE1. TM IV was exquisitely sensitive to mutation with 10 of 23 mutations causing greatly reduced expression and/or activity. The Phe(161) --> Cys mutant was inhibited by treatment with the water-soluble sulfhydryl-reactive compounds [2-(trimethylammonium)ethyl]methanethiosulfonate and [2-sulfonatoethyl]methanethiosulfonate, suggesting it is a pore-lining residue. The structure of purified TM IV peptide was determined using high resolution NMR in a CD(3)OH:CDCl(3):H(2)O mixture and in Me(2)SO. In CD(3)OH: CDCl(3):H(2)O, TM IV was structured but not as a canonical alpha-helix. Residues Asp(159)-Leu(162) were a series of beta-turns; residues Leu(165)-Pro(168) showed an extended structure, and residues Ile(169)-Phe(176) were helical in character. These three structured regions rotated quite freely with respect to the others. In Me(2)SO, the structure was much less defined. Our results demonstrate that TM IV is an unusually structured transmembrane segment that is exquisitely sensitive to mutagenesis and that Phe(161) is a pore-lining residue.
Organizational Affiliation:
Membrane Protein Research Group, Department of Biochemistry, Canadian Institutes of Health Research Group in Protein Structure and Function, and Protein Engineering Network of Centers of Excellence, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada.