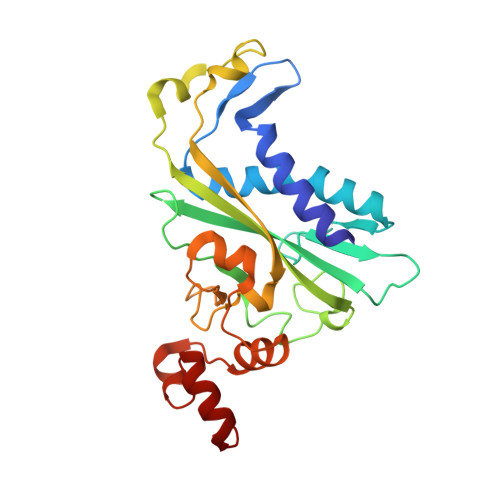
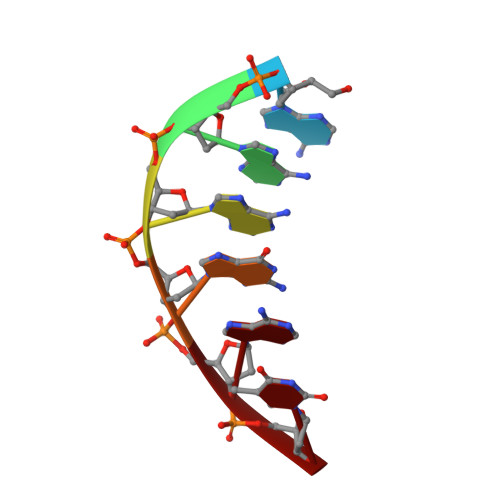
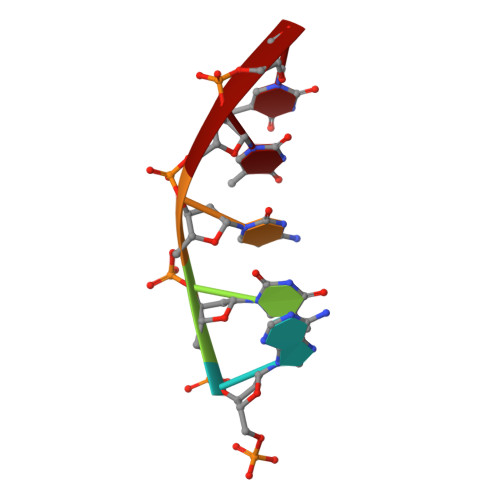
DNA cleavage by EcoRV endonuclease: two metal ions in three metal ion binding sites
Horton, N.C., Perona, J.J.(2004) Biochemistry 43: 6841-6857
- PubMed: 15170321
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0499056
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1STX, 1SUZ, 1SX5, 1SX8 - PubMed Abstract:
Four crystal structures of EcoRV endonuclease mutants K92A and K38A provide new insight into the mechanism of DNA bending and the structural basis for metal-dependent phosphodiester bond cleavage. The removal of a key active site positive charge in the uncleaved K92A-DNA-M(2+) substrate complex results in binding of a sodium ion in the position of the amine nitrogen, suggesting a key role for a positive charge at this position in stabilizing the sharp DNA bend prior to cleavage. By contrast, two structures of K38A cocrystallized with DNA and Mn(2+) ions in different lattice environments reveal cleaved product complexes featuring a common, novel conformation of the scissile phosphate group as compared to all previous EcoRV structures. In these structures, the released 5'-phosphate and 3'-OH groups remain in close juxtaposition with each other and with two Mn(2+) ions that bridge the conserved active site carboxylates. The scissile phosphates are found midway between their positions in the prereactive substrate and postreactive product complexes of the wild-type enzyme. Mn(2+) ions occupy two of the three sites previously described in the prereactive complexes and are plausibly positioned to generate the nucleophilic hydroxide ion, to compensate for the incipient additional negative charge in the transition state, and to ionize a second water for protonation of the 3'-oxyanion. Reconciliation of these findings with earlier X-ray and fluorescence studies suggests a novel mechanism in which a single initially bound metal ion in a third distinct site undergoes a shift in position together with movement of the scissile phosphate deeper into the active site cleft. This reconfigures the local environment to permit binding of the second metal ion followed by movement toward the pentacovalent transition state. The new mechanism suggested here embodies key features of previously proposed two- and three-metal catalytic models, and offers a view of the stereochemical pathway that integrates much of the copious structural and functional data that are available from exhaustive studies in many laboratories.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry and Interdepartmental Program in Biomolecular Science and Engineering, University of California at Santa Barbara, Santa Barbara, California 93106-9510, USA.