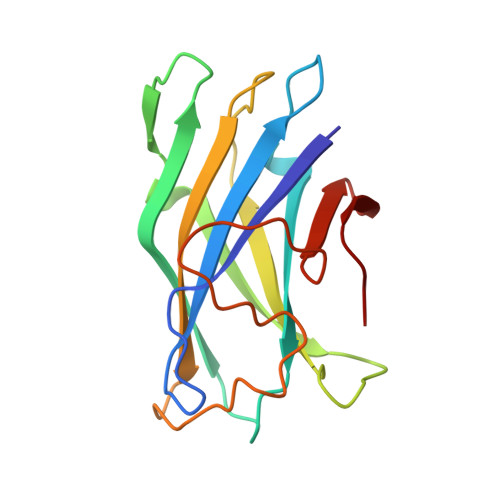
Crystal structure of a bacterial family-III cellulose-binding domain: a general mechanism for attachment to cellulose.
Tormo, J., Lamed, R., Chirino, A.J., Morag, E., Bayer, E.A., Shoham, Y., Steitz, T.A.(1996) EMBO J 15: 5739-5751
- PubMed: 8918451
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1NBC - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of a family-III cellulose-binding domain (CBD) from the cellulosomal scaffoldin subunit of Clostridium thermocellum has been determined at 1.75 A resolution. The protein forms a nine-stranded beta sandwich with a jelly roll topology and binds a calcium ion. conserved, surface-exposed residues map into two defined surfaces located on opposite sides of the molecule. One of these faces is dominated by a planar linear strip of aromatic and polar residues which are proposed to interact with crystalline cellulose. The other conserved residues are contained in a shallow groove, the function of which is currently unknown, and which has not been observed previously in other families of CBDs. On the basis of modeling studies combined with comparisons of recently determined NMR structures for other CBDs, a general model for the binding of CBDs to cellulose is presented. Although the proposed binding of the CBD to cellulose is essentially a surface interaction, specific types and combinations of amino acids appear to interact selectively with glucose moieties positioned on three adjacent chains of the cellulose surface. The major interaction is characterized by the planar strip of aromatic residues, which align along one of the chains. In addition, polar amino acid residues are proposed to anchor the CBD molecule to two other adjacent chains of crystalline cellulose.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA.