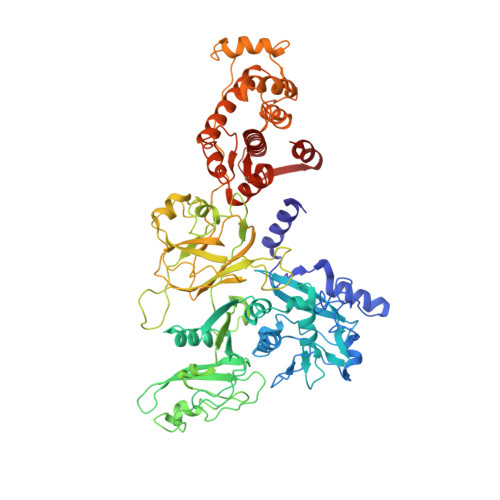
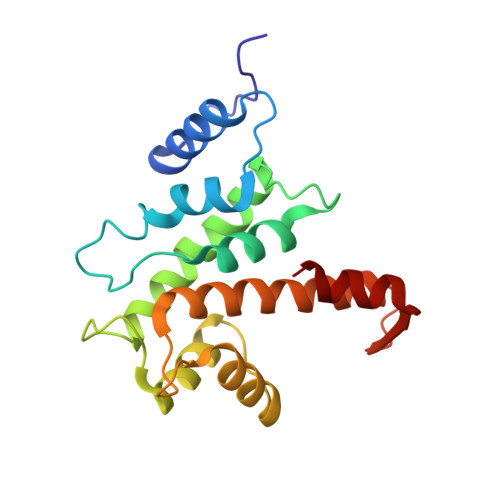
The crystal structure of calcium-free human m-calpain suggests an electrostatic switch mechanism for activation by calcium.
Strobl, S., Fernandez-Catalan, C., Braun, M., Huber, R., Masumoto, H., Nakagawa, K., Irie, A., Sorimachi, H., Bourenkow, G., Bartunik, H., Suzuki, K., Bode, W.(2000) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97: 588-592
- PubMed: 10639123
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.2.588
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1KFU, 1KFX - PubMed Abstract:
Calpains (calcium-dependent cytoplasmic cysteine proteinases) are implicated in processes such as cytoskeleton remodeling and signal transduction. The 2.3-A crystal structure of full-length heterodimeric [80-kDa (dI-dIV) + 30-kDa (dV+dVI)] human m-calpain crystallized in the absence of calcium reveals an oval disc-like shape, with the papain-like catalytic domain dII and the two calmodulin-like domains dIV+dVI occupying opposite poles, and the tumor necrosis factor alpha-like beta-sandwich domain dIII and the N-terminal segments dI+dV located between. Compared with papain, the two subdomains dIIa+dIIb of the catalytic unit are rotated against one another by 50 degrees, disrupting the active site and the substrate binding site, explaining the inactivity of calpains in the absence of calcium. Calcium binding to an extremely negatively charged loop of domain dIII (an electrostatic switch) could release the adjacent barrel-like subdomain dIIb to move toward the helical subdomain dIIa, allowing formation of a functional catalytic center. This switch loop could also mediate membrane binding, thereby explaining calpains' strongly reduced calcium requirements in vivo. The activity status at the catalytic center might be further modulated by calcium binding to the calmodulin domains via the N-terminal linkers.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max-Planck-Institute of Biochemistry, Am Klopferspitz 18a, D 82 152 Planegg-Martinsried, Germany.