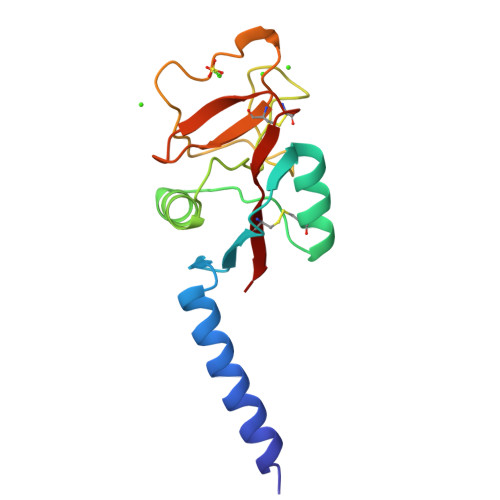
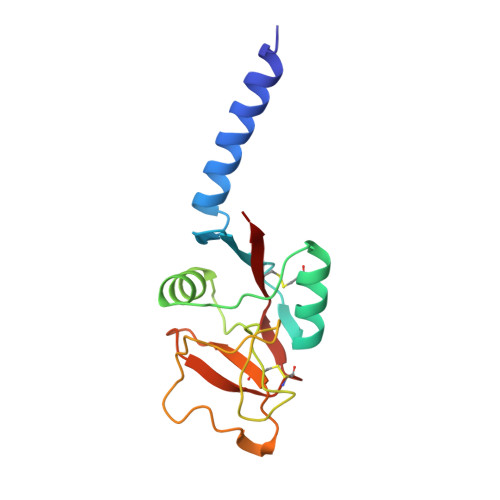
Human mannose-binding protein carbohydrate recognition domain trimerizes through a triple alpha-helical coiled-coil.
Sheriff, S., Chang, C.Y., Ezekowitz, R.A.(1994) Nat Struct Biol 1: 789-794
- PubMed: 7634089
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb1194-789
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1HUP - PubMed Abstract:
Human mannose-binding protein is a hexamer of trimers with each subunit consisting of an amino-terminal region rich in cysteine, 19 collagen repeats, a 'neck', and a carbohydrate recognition domain that requires calcium to bind ligand. A 148-residue peptide, consisting of the 'neck' and carbohydrate recognition domains forms trimers in solution and in crystals. The structure of this trimeric peptide has been determined in two different crystal forms. The 'neck' forms a triple alpha-helical coiled-coil. Each alpha-helix interacts with a neighbouring carbohydrate recognition domain. The spatial arrangement of the carbohydrate recognition domains suggest how MBP trimers form the basic recognition unit for branched oligosaccharides on microorganisms.
Organizational Affiliation:
Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharmaceutical Research Institute, Princeton, NJ 08543-4000, USA.